Press release -
Design of the times: research reveals how the arts can offer vital new approaches to cities’ emergency preparedness and resilience planning
A new report demonstrates ways in which arts practice and performance research methods can provide vital new approaches to city pandemic planning, both in the context of Covid-19 and for future crises.
Covid-19 has transformed the ways in which we live and work in cities. As a result, there is an urgent need to understand how to practise, make sense of and sustain city life in the context of pandemic prevention measures.
At the same time, and in the light of the pandemic, emergency planning professionals are calling for new and novel approaches to preparedness and response planning.
To address these needs, Dr Patrick Duggan from Northumbria University, Newcastle upon Tyne, and Dr Stuart Andrews from Brunel University London are investigating the ways that arts and performance can open up new perspectives on city emergency and resilience strategy and practice.
The 18-month project, funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC) as part of UK Research and Innovation’s rapid response to Covid-19 fund, began in December 2020. In an interim report published yesterday, the academics explain their findings so far, highlighting evidence of how performance practices can respond creatively, swiftly and engagingly to changing situations, while offering ways of sustaining communities’ emotional wellbeing.
The report offers city councils in the UK and internationally a series of ‘invitations to innovate’ that offer means of addressing five pandemic challenges: reaching communities, re-designing places, engaging people with public health messaging, managing perceptions of Covid-19 and vaccinations, connecting people to alleviate isolation and loneliness.
In publishing this report now, and sharing emerging findings, the researchers seek to begin a conversation in the UK and beyond on the ways that ‘performance’ might offer new methods and new ways of thinking about emergency and resilience planning.
Helen Hinds, Head of Resilience Planning, Newcastle City Council, said: “This report is exciting because it reveals new ways of thinking about arts practice in a city, and invites emergency and resilience professionals to develop new modes of pandemic response. Such work is important to the Emergency Planning community because it promotes innovation which develops and changes our professional practice. This can give us better tools to provide a more nuanced response for our communities if an emergency happens.”
Performance, Arts Practice and Emergency Planning
Covid-19 has underlined the vital role that arts practitioners play in identifying and responding to local and city challenges both creatively and at speed. Throughout the pandemic, artists, arts organisations and networks have been responding imaginatively to restrictions, rethinking familiar places and practices, and creating entirely new modes of engagement with local and city communities.
Over the past nine months Dr Duggan and Dr Andrews have been working with strategic decision-makers in hazard mitigation, sustainability and resilience from Bristol, Glasgow and Newcastle City Councils, as well as with artists and arts organisations to explore ways that artistic practice and research might inform hazard mitigation planning in UK cities for the ongoing pandemic and potential future crises.
In the new report, they argue that cities with developed creative infrastructures and cultural life are already prepared to tackle crises because they are likely to have creative and engaging means to intervene in pandemic responses.
Reworking Places
During the research, academics identified a powerful example in Bristol, where the city’s ‘parks with hearts’ – giant, socially distanced hearts painted on the grass – proved to be an engaging way of encouraging people to enjoy green spaces safely. This simple yet appealing intervention sparked a flurry of social media engagement, further promoting physical distancing in the city, while simple circles painted in other cities’ public spaces were found to be less effective.
Dr Duggan, Associate Professor of Performance and Culture at Northumbria University, explained: “Performative, playful and creative interventions in cities during the pandemic invite new ways of encountering with public safety protocols that are engaging and, potentially, even fun. This offers opportunities for innovative thinking in emergency planning.”
Visit Bristol’s 'parks with hearts', part of their #LoveBristol campaign, created by a group of artists from Upfest, Europe's largest live street art festival.
In another compelling case, Slung Low, an award-winning theatre company in Holbeck, Leeds, allowed for moments of joy in a challenging period of restricted living. Early in the UK’s first lockdown, the company curated a street exhibition, offering physically distanced entertainment to those in the area. The exhibition was made up of pictures created by local residents that were attached to lampposts for people to discover during their daily exercise.
The same company also hosted a volunteer-led foodbank, and in June 2020 they produced a Covid-secure outdoor theatre performance. Family bubbles watched from individual tents and listened in through headphones as actors performed on the back of a flatbed truck in a carpark.
Dr Andrews, Lecturer in Theatre at Brunel University London, reflects: “A key element of this research is that it focuses on arts and emergency planning practices that are already operating in cities. The work of the project is to identify these practices and invite practitioners from these apparently separate fields to join us in a conversation, where we begin to explore ways of thinking differently about pressing challenges. The report shares this process and our initial findings beyond our case study cities and invites colleagues in and beyond these cities to get in touch to reflect on the work.”
Creative approaches to public health messaging
Through interviews and committee meetings with officers from Bristol, Glasgow and Newcastle City Councils, as well as gathering anecdotal and observational evidence, the researchers found that conventional municipal Covid-19 signage was not always effective. The researchers identified examples of arts practice that reworked public health messaging to emphasise creative engagement with the needed message.
Outside BALTIC Centre for Contemporary Art, an art gallery on the bank of the River Tyne in Gateshead, words from public messaging have been included in a public artwork painted on the flagstones: ‘Hands, Face’, ‘Save’. Participants can observe the signs but also encounter them through following the swirling lines of the artwork. The artwork, Rainbow’s End by Zoe Allen and Allan Dixon, both fragments familiar public health messaging but also invites new readings of the familiar words and places them in relation with other messages about climate emergency and the fate of the bees.
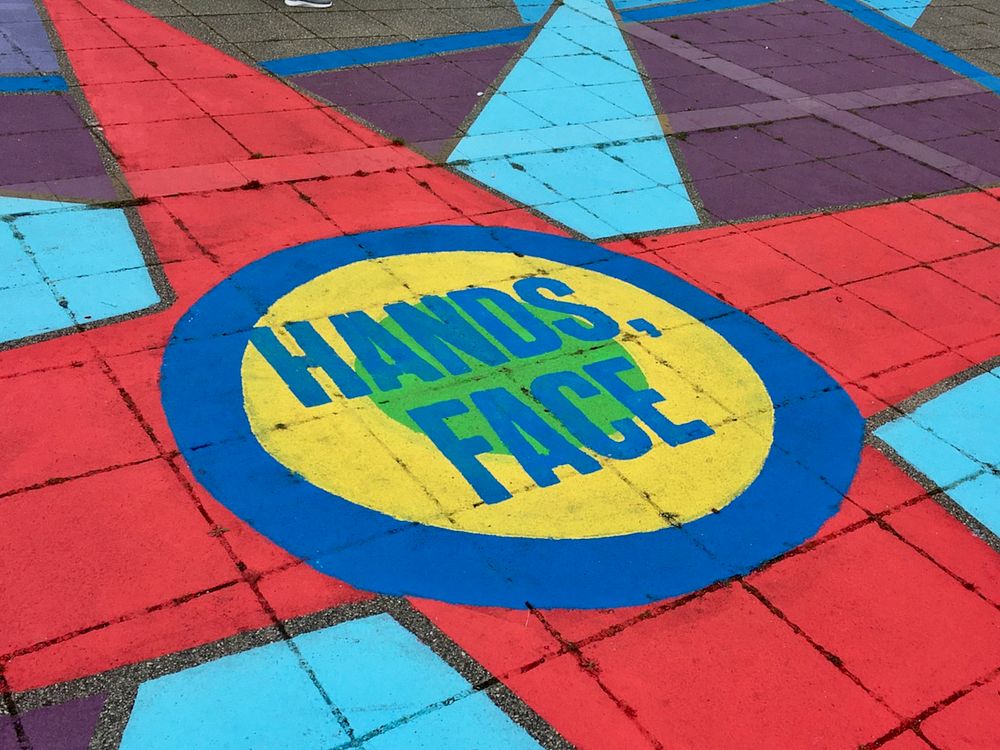

'Rainbow’s End', by Zoe Allen and Allan Dixon, BALTIC Centre for Contemporary Art, August 2021. Image by Dr Stuart Andrews.
In Glasgow, The Hidden Gardens provide urban greenspace where people can escape the busy city streets. Here, a reminder of Covid rules and measures could be found illustrated on a chalkboard, partially hidden behind planting for visitors to discover on arrival. The interactive nature of this approach was observed to be effective in inviting people to read and take note of the guidance.
Through the next months of the project, the team will be engaging in conversation with colleagues in the arts and those in emergency response and resilience preparedness about the findings and they will reflect on their potential usefulness in developing city pandemic strategy.
For more information about the project please visit www.performingcityresilience.com
-Ends-
Notes to editors:
This research is supported by funding of over £120,000 received through the Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC) as part of UK Research and Innovation’s rapid response to Covid-19 fund – set up to support projects which contribute to our understanding of, and response to, the Covid-19 pandemic and its impacts.
The full report can be found here: https://performingcityresilience.com/publications/
The research has also been distilled into a recent article for Crisis Response Journal: https://www.crisis-response.com/Publisher/Article.aspx?ID=617774
Topics
Categories
Northumbria is a research-rich, business-focused, professional university with a global reputation for academic excellence. Find out more about us at www.northumbria.ac.uk --- Please contact our Media and Communications team at media.communications@northumbria.ac.uk with any media enquiries or interview requests ---