News -
NGK Expands Ceramic Technology into Direct Air Capture for Carbon Neutrality
NGK Insulators, Ltd. announced new progress in applying its century-long ceramic technology expertise to Direct Air Capture (DAC), a key solution for achieving global carbon neutrality by 2050. At a media briefing held at the company’s headquarters in Nagoya, NGK presented its proprietary DAC innovations and discussed their role in the future energy transition.
The briefing featured presentations by Nobuo Tanaka, Honorary Executive Director of the International Energy Agency (IEA), and Professor Hidetaka Yamada of Kanazawa University on global energy trends and DAC developments, alongside NGK’s latest advancements.
Expert Insights on DAC Technology's Critical Role
In his opening keynote, Nobuo Tanaka emphasized that for resource-constrained nations like Japan, carbon removal technologies such as CCS (Carbon Capture and Storage) and DAC (Direct Air Capture) are gaining critical importance.
He also pointed out that achieving both energy security and carbon neutrality requires strategic deployment of clean hydrogen, ammonia, small modular reactors, and other emerging technologies.
According to IEA's net-zero scenario, achieving global carbon neutrality requires 2.5 Gt of CCS and 1.2 Gt of DAC by 2050. "If Japan can lead the world in DAC technology, it can gain strategic advantages in both energy security and climate action," Tanaka stated, underscoring how carbon removal technologies can serve as a cornerstone for balancing resource security with environmental commitments.

Mr. Tanaka explaining global energy situation and environmental crisis
Professor Hidetaka Yamada of Kanazawa University explained DAC's critical importance under the premise that "achieving 2050 carbon neutrality requires both emission reduction and removal." He pointed out limitations of natural removal methods like afforestation in terms of required scale (land area), growth speed, and reliability, highlighting DAC's potential among negative emission technologies with the following advantages:
Key Advantages of DAC as a Removal Method:
- Measurement Clarity: Enables precise quantification of CO2 removal volumes
- Location Flexibility: Not constrained by forest area limitations
- Processing Speed: Dramatically faster than natural processes
- Quality Consistency: High purity of captured CO2
Professor Yamada identified the primary challenge as high removal costs (US$ 500–1,000/t). "The main cause of these high costs is the enormous energy consumption required to process extremely dilute 0.04% CO2 in ambient air," he analyzed. "Fan power for circulating large volumes of air and thermal energy for sorbent regeneration account for the majority of overall costs."
He projected cost reduction to US$ 100-200 per ton by the 2030s through technological innovations including significant pressure loss reduction and improved sorbent performance.
Professor Yamada noted that current DAC technologies split between liquid absorption methods (20%) and solid adsorption methods (70%). While liquid systems offer fast reaction speeds, they require high energy for solution circulation and face corrosion issues. Solid adsorption systems operate at lower temperatures (80-120°C) but face a critical challenge: "Fan power accounts for 50-60% of total system energy consumption due to pressure losses."
He emphasized DAC's strategic importance beyond carbon removal: "DAC technology will be decisively important as a carbon resource supply source in future carbon-neutral society," positioning it as fundamental for chemical industry and fuel manufacturing.
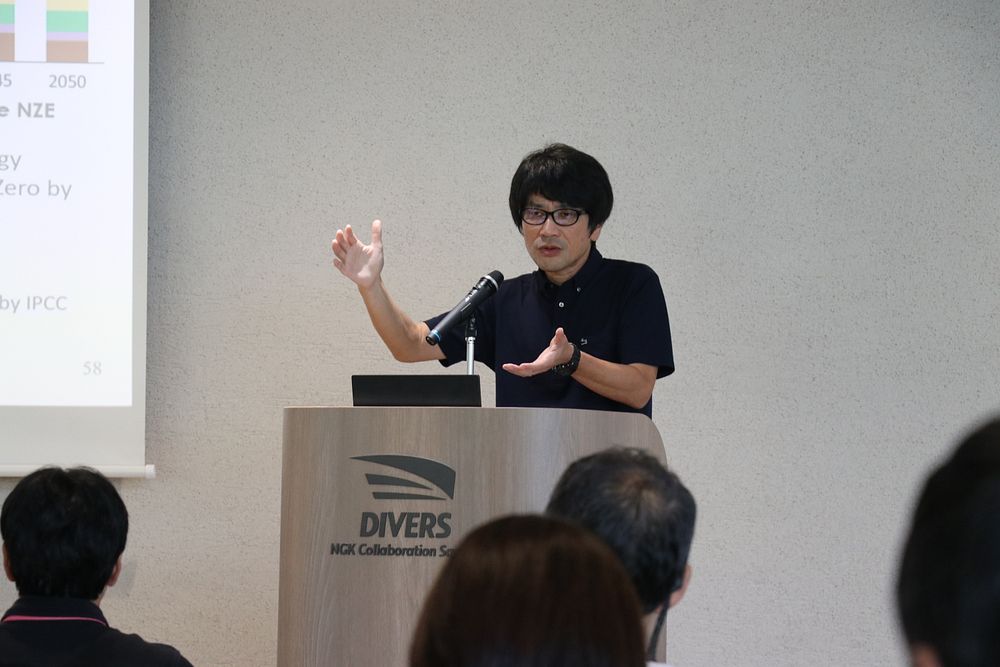

Professor Yamada explaining the importance and challenges of DAC technology and global trends
NGK's Technology Innovation and Business Strategy
Leveraging Over 100 Years of Ceramic Technology
NGK Insulators provided a comprehensive explanation of its DAC technology development efforts. Motoo Noritake, Group Executive of Environment Business Group, outlined NGK's history of expanding its business based on ceramic technology since its 1919 founding, beginning with electrical insulators. "We are actively developing new businesses leveraging existing technologies, focusing on two major growth areas: carbon neutrality and digital society," he stated.
From a management perspective, Noritake emphasized that "the expertise in automotive exhaust purification technology that we have cultivated provides decisive advantages in our DAC technology development." He revealed that NGK is preparing to shift existing automotive production facilities toward carbon neutrality-related businesses in response to expanding DAC demand.
NGK Executive Noritake explaining how expanding automotive operations support DAC technology
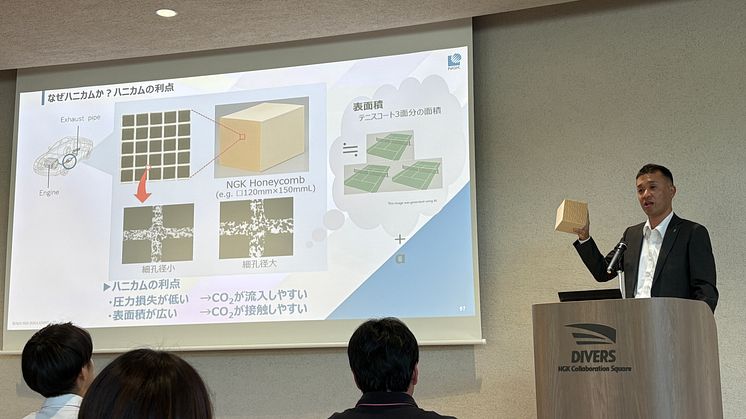
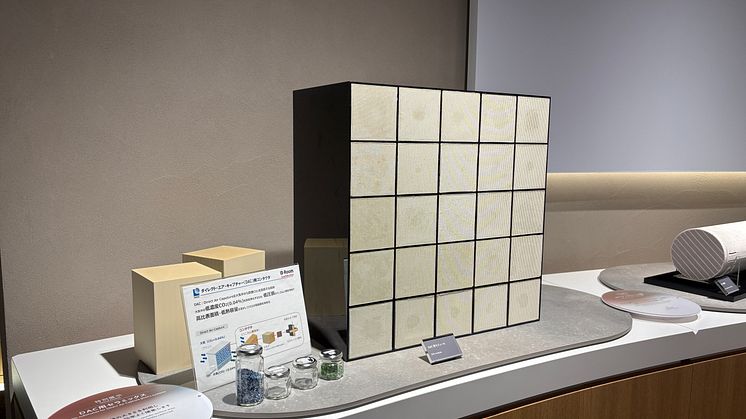
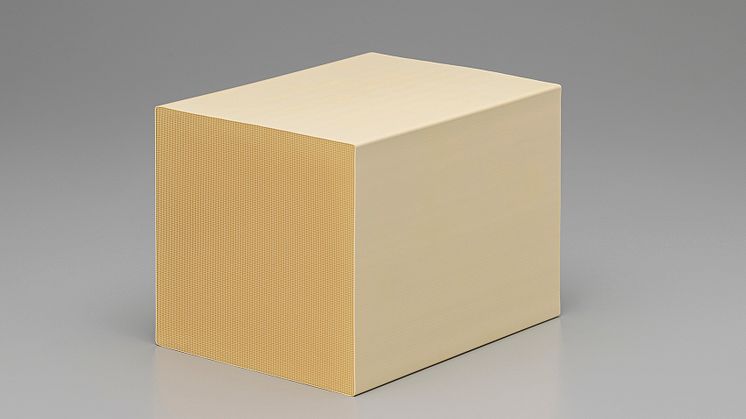
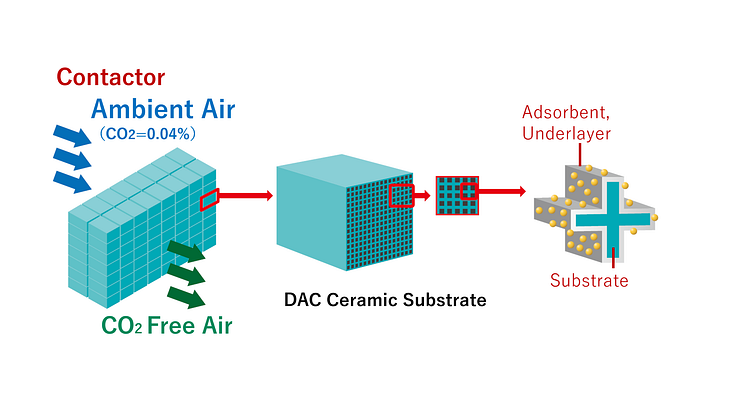
NGK's honeycomb structures for DAC
Masataka Yamashita, Senior Director of Environment Business Group detailed NGK's DAC honeycomb structures that solve pressure loss bottlenecks while improving efficiency.
Conventional pellet systems create turbulent flow and significant pressure loss. NGK's honeycomb structures maintain laminar flow through regular channels, dramatically reducing pressure loss. The thin-wall structure—approximately tissue paper thickness—enables efficient regeneration at 80-100°C.
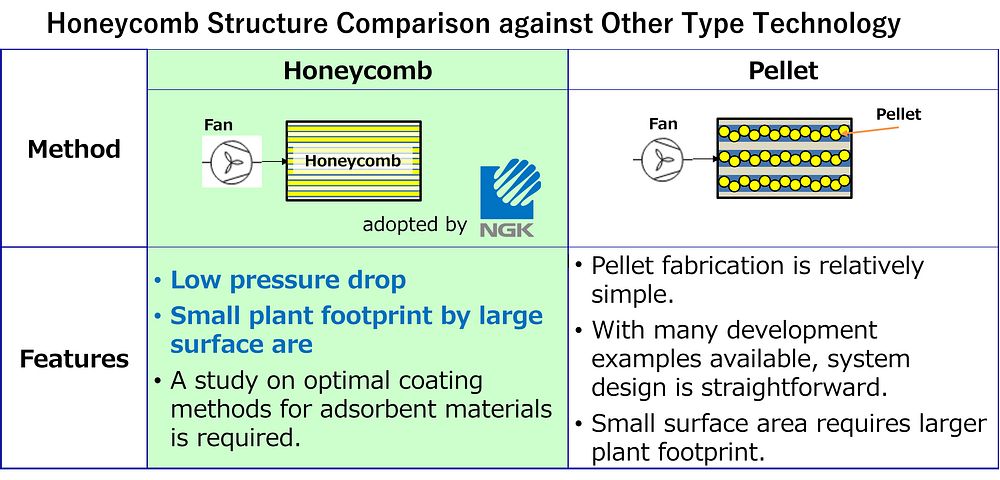
Key Technical Advantages:
- Large Surface Area: Regular thin-wall arrangement achieves surface area equivalent to 3+ tennis courts
- Low Pressure Loss: Efficient processing of large air volumes
- Energy Efficiency: Significant reduction in overall system energy consumption
- Proven Manufacturing: Based on automotive exhaust purification technology
In existing automotive exhaust gas purification ceramic technology, honeycomb structures and pellet types were compared during the early market development phase. However, honeycomb structures ultimately became mainstream from the perspective of achieving both purification performance and pressure loss reduction. "Similarly, efficient capture of extremely dilute 0.04% CO2 requires compact structures with large surface areas," Yamashita explained. "Our ceramic technology know-how in 'thin walls, large surface area, low pressure loss' creates competitive advantages in DAC."
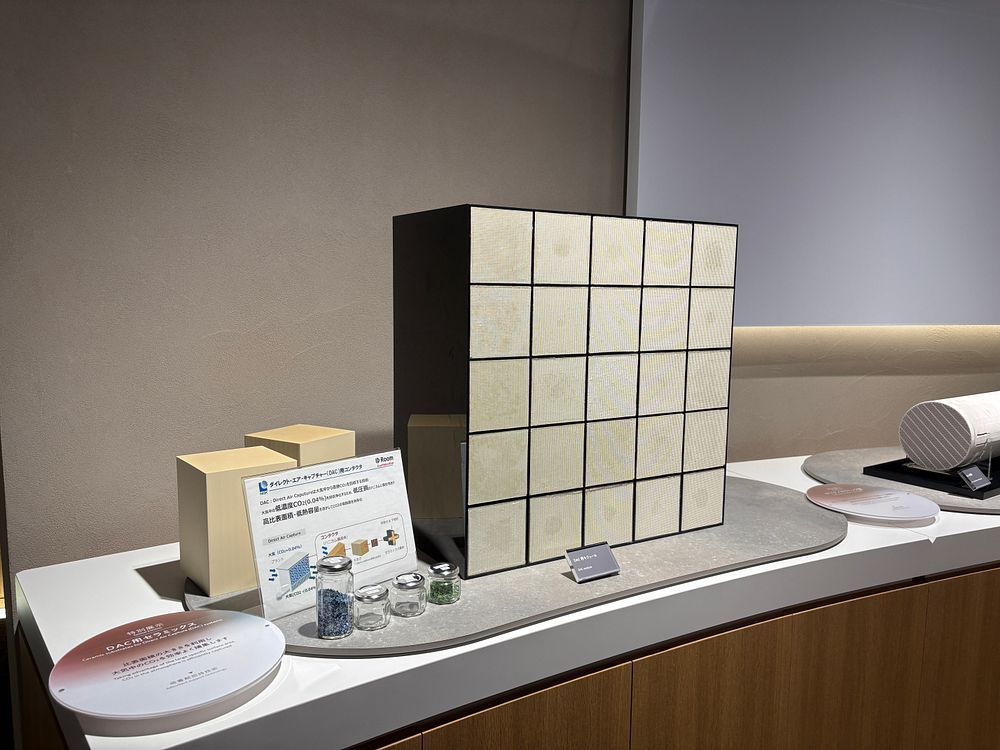


NGK's DAC honeycomb structures with thin walls arranged in regular patterns
Global Market Development and Future Outlook
NGK is in discussions with over 30 manufacturers worldwide and has received demonstration requests from multiple companies. "Large-scale demonstrations and commercialization are expected from 2030 onward," Yamashita noted, revealing parallel advancement of technology development and production preparation.
The company is preparing to shift existing automotive facilities toward carbon neutrality applications and collaborates with Japan CDR Coalition led by Mitsubishi Corporation to promote DAC adoption.
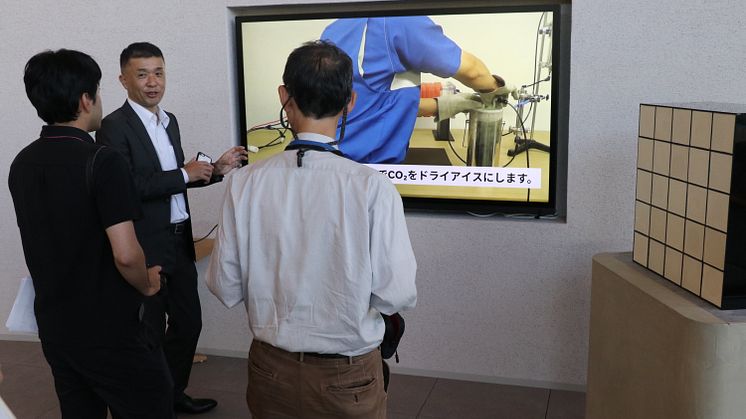
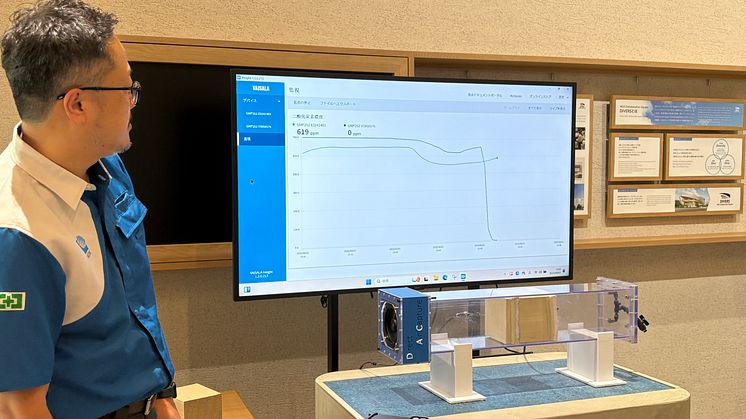
Live demonstrations showed CO2 concentrations dropping to near zero as ambient air passed through NGK's honeycomb structures, providing tangible proof of effectiveness.
As global demand for negative emission technologies intensifies, NGK's ceramic technology expertise positions the company as a key player in achieving worldwide carbon neutrality.
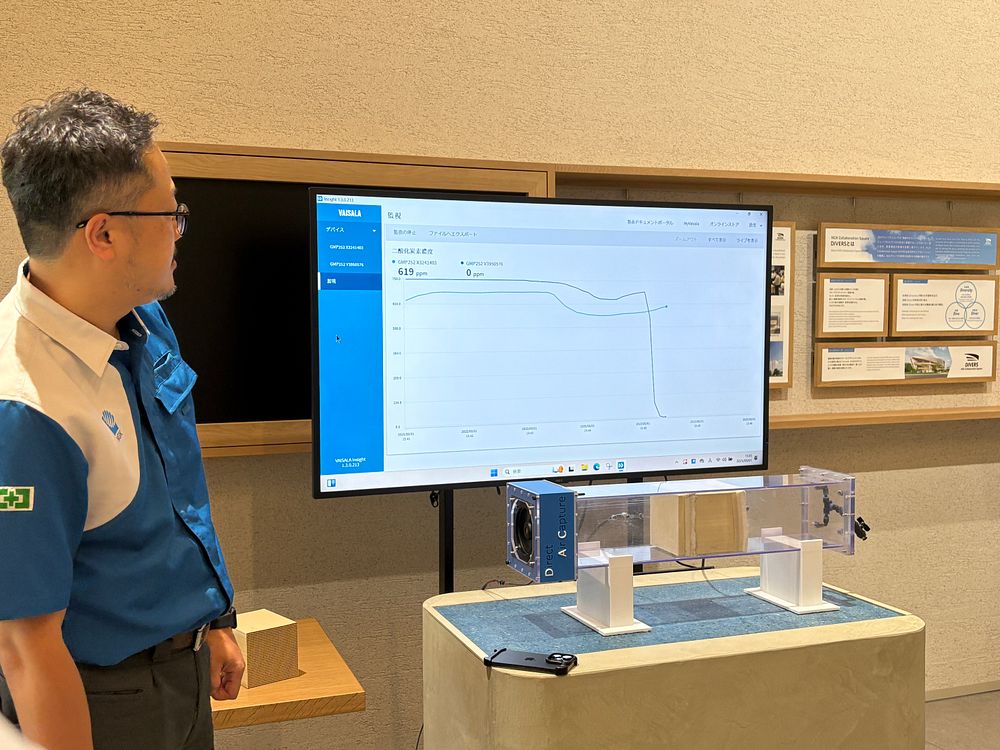

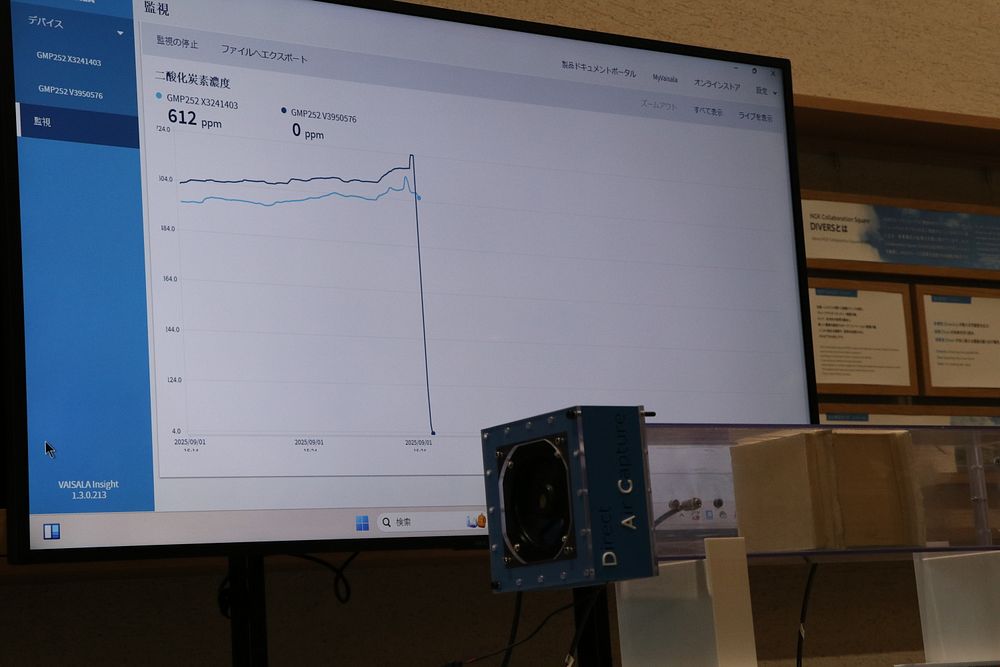
Live demonstration showing CO2 concentration dropping to near zero as ambient air passes through NGK's DAC honeycomb structures
About NGK Insulators
NGK Insulators (NGK) is a leading company in the field of ceramics. Since its foundation in 1919, NGK has used its unique ceramic technology to provide numerous ground-breaking products that solve social issues. Today, NGK is active in more than 20 countries worldwide, with business foci including mobility, energy, IT and industry.
As one of the largest manufacturers of ceramic substrates for automotive catalytic converters, NGK is actively reducing the strain on our global environment. Furthermore, NGK’s products include the energy storage system “NAS” battery, in addition to the compact, thin and high-energy-density lithium-ion rechargeable “EnerCera” battery line, vital tools for sustainable energy infrastructure.
Through providing innovative, high-quality products, NGK is committed to contributing to our society. In order to create a future where people can coexist with nature, we will continue to develop and provide products that support social infrastructure while preserving the environment.