Press release -
Yanmar and Faeger Submit Project Design Document and Monitoring Report Aiming to Launch the World’s First Compliance Credits in the Agricultural Sector
Osaka, Japan (June 13, 2025) – Yanmar Agribusiness Co., Ltd. (Yanmar Agri), a group company of Yanmar Holdings, and its local subsidiary, Yanmar Philippines Corporation (Yanmar Philippines) have submitted the Project Design Document (PDD) and the first monitoring report to the Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) Secretariat. The submission is part of a decarbonization initiative in Luzon, the Philippines, jointly implemented with Faeger Co. Ltd. (Faeger).
These documents represent an important step toward the issuance of compliance credits—carbon credits that can be used under official schemes led by national or international authorities to meet greenhouse gas reduction targets such as NDCs1. Under the JCM, once the submitted PDD and monitoring report are reviewed and deemed appropriate, the project becomes eligible for credit issuance. The approval will signify progress toward the world’s first issuance of compliance credits in the agricultural sector.
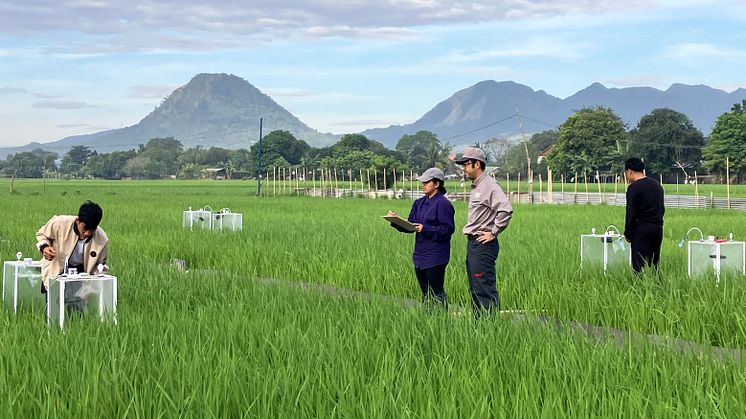
The JCM project jointly undertaken by Yanmar and Faeger, first announced in June 2024, aims to reduce methane emissions from rice paddies in the Philippines by introducing Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD), a water management technique that helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions by optimizing irrigation in rice paddies.
Project Overview
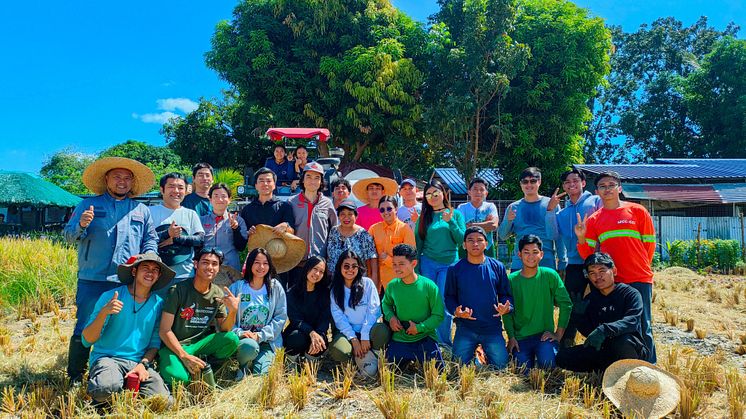
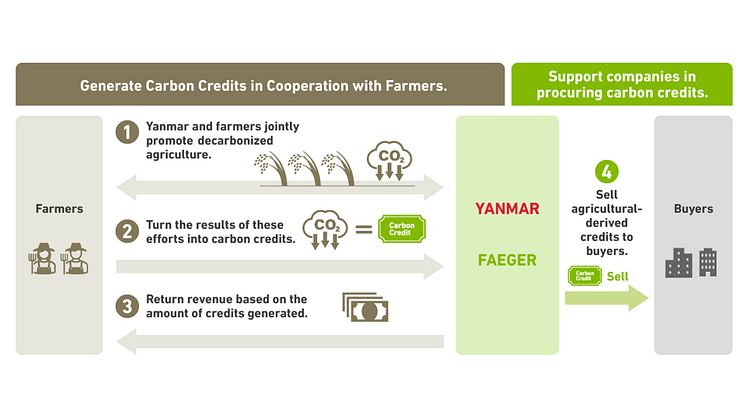
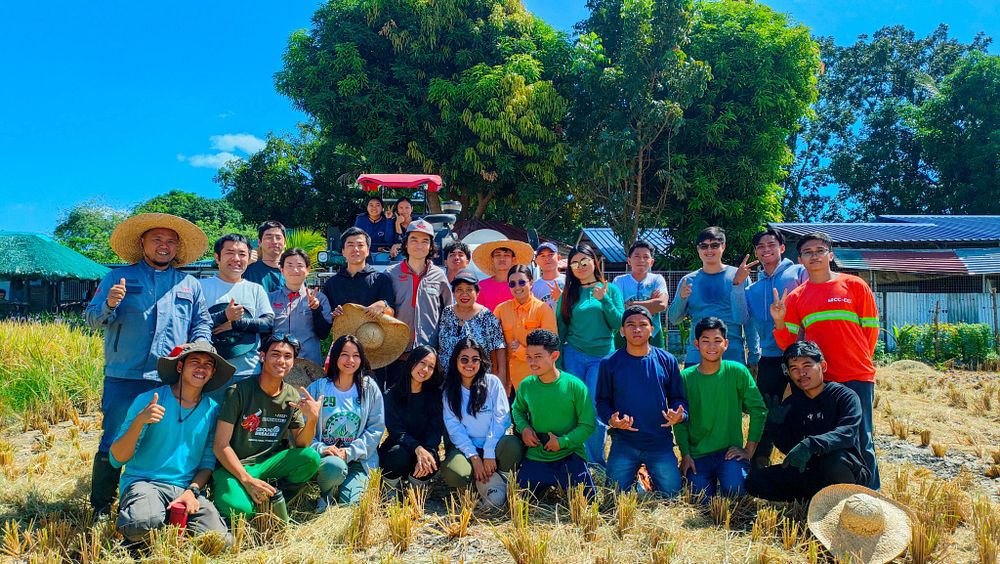
This project combines the Yanmar Group’s agricultural machinery and related solutions with Faeger’s expertise and proven achievements in rice cultivation and carbon credit generation in Japan. In collaboration with the Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice), the project will conduct a joint research project as part of its efforts to adapt and validate the implementation of AWD technologies in local conditions. It aims to create locally impactful outcomes based on the international cooperation framework of the Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM), with Yanmar and Faeger playing a central role in driving the initiative to deliver lasting value to the agricultural sector even beyond the life of the project. It also aims to serve as a model for decarbonization projects globally, beyond Japan and the Philippines.
To date, Yanmar Agri, Yanmar Philippines, and Faeger have worked closely with local farmers, municipal governments, and Philippine government agencies to support the introduction of AWD, monitor field data, and design incentive mechanisms. Moving forward, the partners will continue collaborating with the Japanese and Philippine governments and local farmers to issue JCM credits and increase yields through comprehensive guidance on rice cultivation techniques not limited to AWD, with the aim of achieving food security and sustainable agriculture in the Philippines.

About the Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM)
The JCM is a bilateral framework in which Japan collaborates with developing countries to implement greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction projects. The resulting emission reductions are credited to both countries and count toward their respective NDCs under the Paris Agreement.
Reference:
https://www.mofa.go.jp/ic/ch/page1we_000105.html
About Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD)
AWD is a water management technique used in rice cultivation. Rice paddies in the Philippines are typically continuously flooded, which promotes the activity of methane-producing bacteria in the soil. AWD involves periodically drying the rice paddies and supplying oxygen to the soil, thus inhibiting the activity of these bacteria and reducing methane emissions compared to constant flooding.
Additionally, conventional rice cultivation requires a large amount of water to maintain the flooded state, which poses a challenge in regions with insufficient water resources. AWD significantly reduces water usage by intermittently drying the paddies. It is also expected to reduce fuel consumption by water pumps2. This method is gaining attention for its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
1: NDC stands for Nationally Determined Contribution, which refers to the greenhouse gas reduction targets and measures that each country voluntarily sets under the Paris Agreement adopted in 2015.
2: The National Agriculture and Food Research Organization: Alternate wetting and drying reduces methane emission from irrigated rice paddy field in Southeast Asia (Japanese)
https://www.naro.go.jp/project/results/4th_laboratory/niaes/2017/niaes17_s12.html
About Yanmar
With beginnings in Osaka, Japan, in 1912, Yanmar was the first ever to succeed in making a compact diesel engine of a practical size in 1933. A pioneer in diesel engine technology, Yanmar is a global innovator in a wide range of industrial equipment, from small and large engines, agricultural machinery and facilities, construction equipment, energy systems, marine, to machine tools, and components — Yanmar’s global business operations span seven domains. On land, at sea, and in the city, Yanmar provides advanced solutions to the challenges customers face, towards realizing A Sustainable Future. For more details, please visit the official website of Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
https://www.yanmar.com/global/about/
About Faeger
Faeger is a company that collaborates with farmers to generate carbon credits. It is one of the few companies in Japan that can consistently handle everything from the creation to the sale of carbon credits. Faeger provides these credits to business as "credits that show the face of producers committed to decarbonization", providing value not only through carbon offsets but also in public relations. By supporting the process of credit creation and purchasing, Faeger brings revenue to farmers and promotes activities to reduce CO2 emissions in agriculture.
https://faeger.company/en/
Related links
Topics
Categories
Note: Information contained in the news release is valid at the time of publication and may differ from the most recently available information.
[Inquiries for further information]
Corporate Communications, Yanmar