Nyhet -
Autonomous vehicles for ecosystem monitoring in the Arctic
New publication from the Akvaplan-niva led GLIDER project recently published in the journal "Sensors". Manager of Digital Solutions at Akvaplan-niva, Lionel Camus, is the first author of the paper.
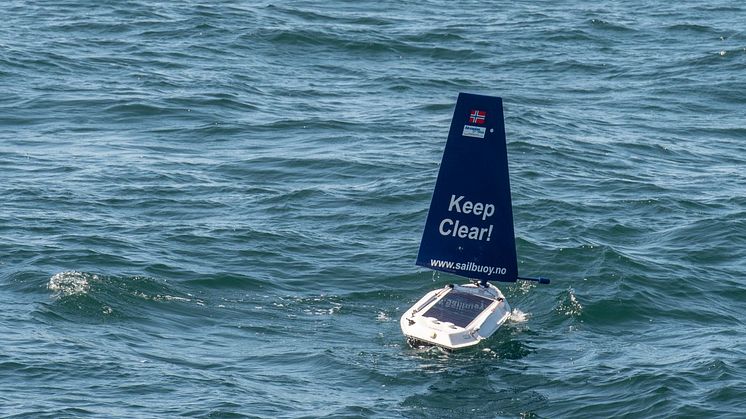
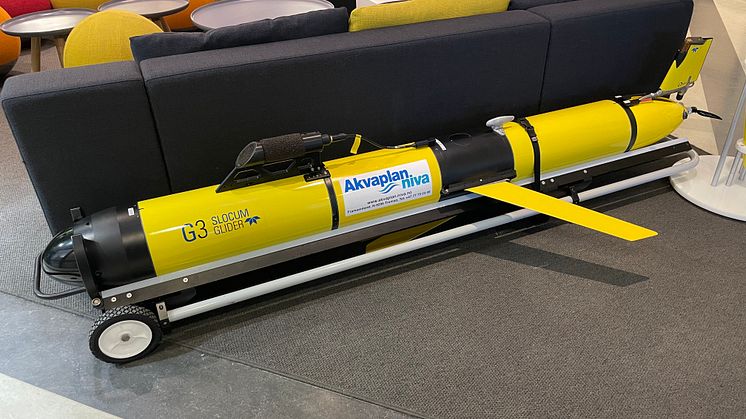
Effective ocean management requires integrated and sustainable ocean observing systems enabling us to map and understand ecosystem properties and the effects of human activities. Autonomous subsurface and surface vehicles, here collectively referred to as “gliders”, are part of such ocean observing systems providing high spatiotemporal resolution.
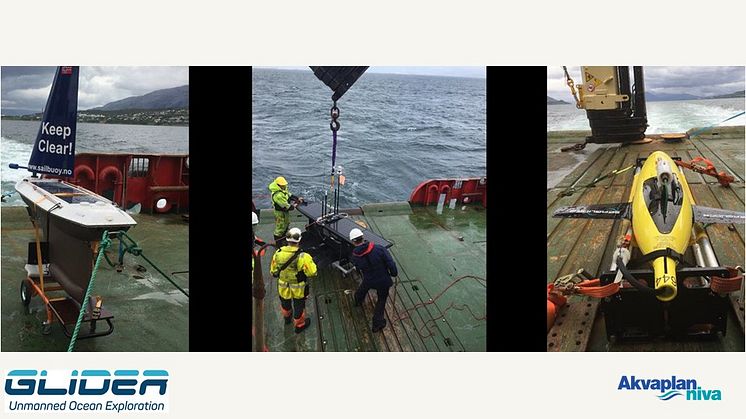
In a recently published paper, a team of scientists and technology developers presents some of the results achieved through the project “Unmanned ocean vehicles, a flexible and cost-efficient offshore monitoring and data management approach—GLIDER”. In this project, three autonomous surface and underwater vehicles were deployed along the Lofoten–Vesterålen (LoVe) shelf-slope-oceanic system, in Arctic Norway. The aim of this effort was to test whether gliders equipped with novel sensors could effectively perform ecosystem surveys by recording physical, biogeochemical, and biological data simultaneously.
From March to September 2018, a period of high biological activity in the area, the gliders were able to record a set of environmental parameters, including, temperature, salinity, and oxygen, map the spatiotemporal distribution of zooplankton, and record cetacean vocalizations and anthropogenic noise. A subset of these parameters was effectively employed in near-real-time data assimilative ocean circulation models, improving their local predictive skills. The results presented in the recent publication demonstrate that autonomous gliders can be effective long-term, remote, noninvasive ecosystem monitoring and research platforms capable of operating in high-latitude marine ecosystems. Accordingly, these platforms can record high-quality baseline environmental data in areas where extractive activities are planned and provide much-needed information for operational and management purposes.
Link to publication: https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220...