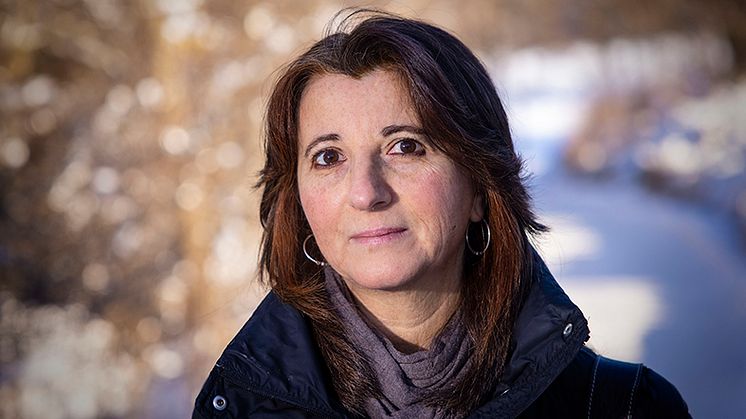
Stefania Barca the new visiting Zennström climate professor
Stefania Barca, from the University of Coimbra in Portugal, is to be Uppsala University’s fourth Zennström Professor of Climate Change Leadership. In her research, she focuses particularly on issues of justice connected with environmental and climate change.