The focus of financial reporting influences business cycles
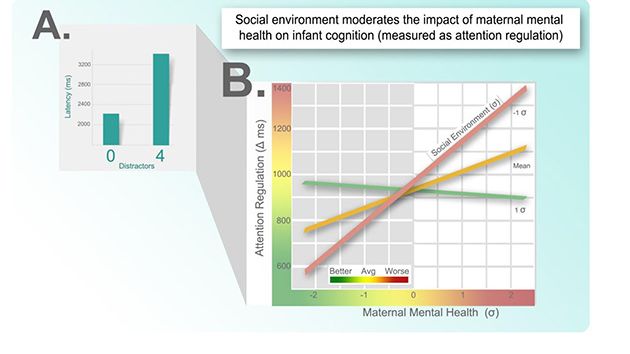
Editorial choices can impact the amplitude of business cycles even if the information that is reported is correct. On reason is that the focus of the reports can be on sectors that are non-representative of the economy in general. A new study shows that financial reporting can explain up to 20 per cent of the business cycles for GDP and 40 per cent of the business cycles for unemployment.