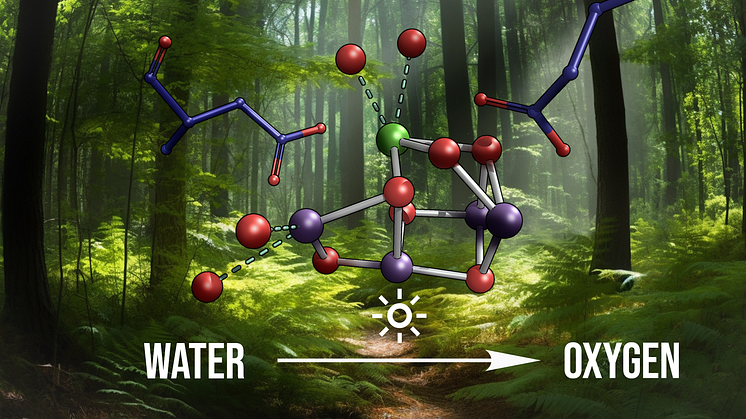
XFELs show the final milliseconds of oxygen formation
Using serial femtosecond crystallography performed with the XFEL technique, scientists have been able to see the crucial final step in the reaction cycle of Photosystem II, and managed to obtain more information on the interaction between Photosystem II and the Mn/Ca cluster. "Such a development is important for scaling up hydrogen production from water by sunlight or renewable electricity."