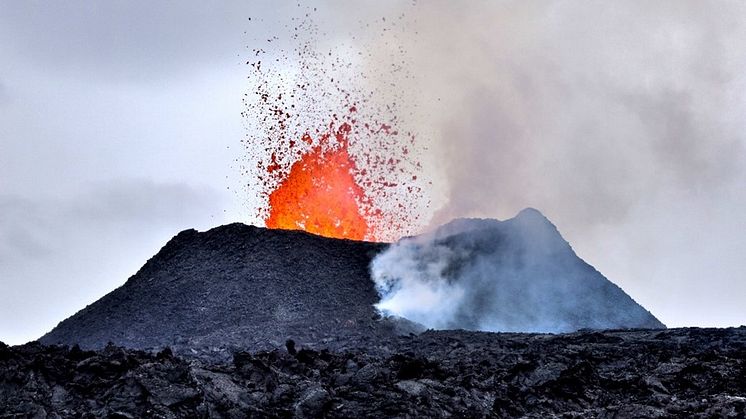
Potential long-term volcanic activity on Iceland's Reykjanes Peninsula
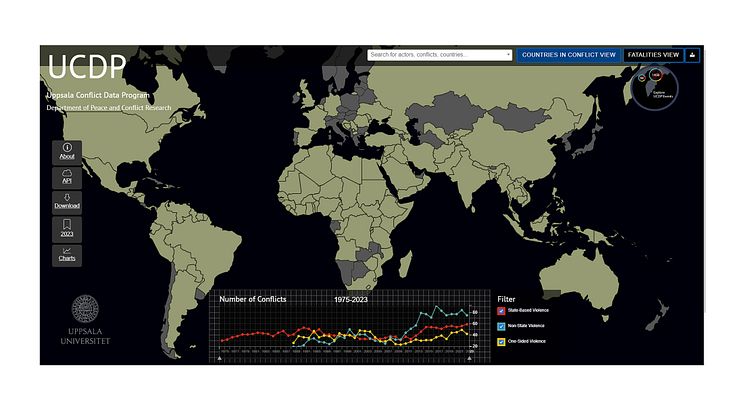
Given the volcanic activity on Iceland over the last three years, researchers from six universities anticipate recurring, moderately sized eruptions of similar style in the coming years to decades. They therefore stress the need for preparedness in view of the risks posed to local populations and critical infrastructure. Their study was recently published in the scientific journal Terra Nova.