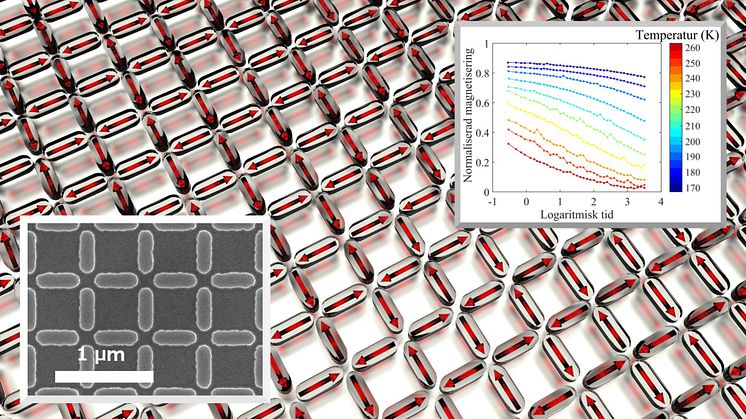
Collective dynamics in magnetic nano-structures
Researchers at the Division of Solid-state Physics and the Division of Material Physics at Uppsala University have shown how the collective dynamics in a structure consisting of interacting magnetic nano-islands can be manipulated. Their findings are published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports