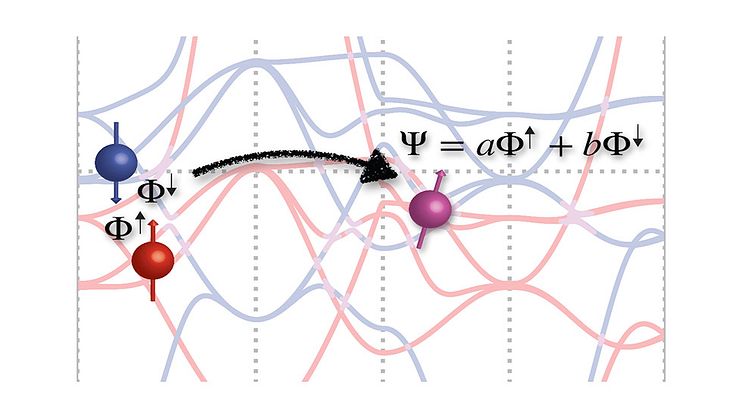
Spin Mixing in Ferromagnets Revealed
For the first time through experiments and theory, Uppsala researchers, together with international collaborators, have been able to measure spin mixing in a ferromagnetic material. Through the experimental measurements, they discovered that a common factor in spin equations, in common use since the 1950s, has been significantly underestimated.
In addition to the well known electric charge, ele