First evidence of feathered polar dinosaurs found in Australia
A cache of 118 million-year-old fossilized dinosaur and bird feathers has been recovered from an ancient lake deposit that once lay beyond the southern polar circle.
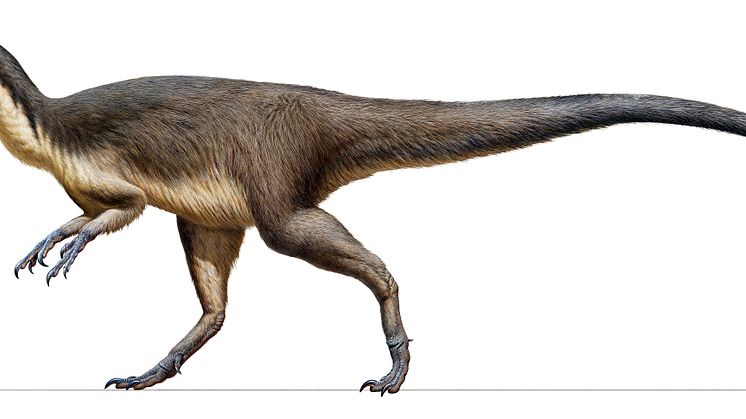
A cache of 118 million-year-old fossilized dinosaur and bird feathers has been recovered from an ancient lake deposit that once lay beyond the southern polar circle.

Superbly preserved fossils from Russia, excavated with support of a grant from the National Geographic Society and described today by an international team in the leading scientific journal Nature, cast new and surprising light on one of the earliest tetrapods – the group of animals that made the evolutionary transition from water to land.
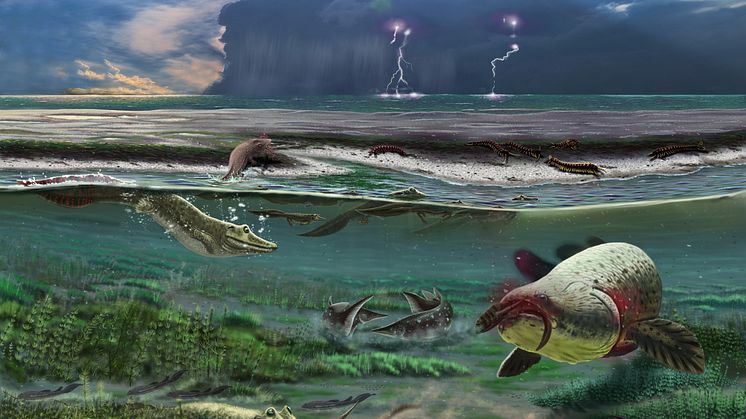

In the ancient Bergslagen ore province of central Sweden lies a zone of ‘Bastnäs-type’ rare earth element deposits, and in a new study, scientists from Uppsala University and the Geological Survey of Sweden (SGU) show how these deposits originally formed.
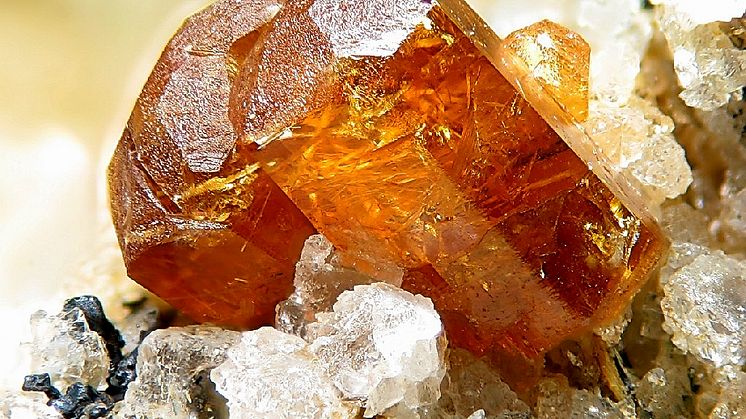

The problem of access to safe drinking water in most parts of Bangladesh is a persistent challenge. Now, a team of scientists shows that a locally growing and previously unexploited green macroalgae species could be used to extract cellulose nanofibers, which can then be formed into paper sheets with tailored pore size that are utilized for point-of-use water treatment.
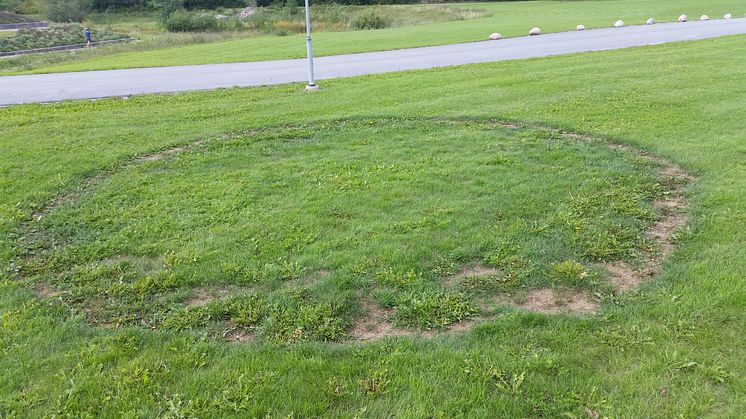
Long-lived mushrooms that grow in ‘fairy rings’ accumulate surprisingly few mutations over time. This finding indicates that their protection against harmful mutations is well developed. The results, to be published in the esteemed journal Current Biology, are interesting in terms of both medicine and evolutionary biology.

For the first time, researchers have demonstrated the creation of a beam of nanodroplets capable of delivering a variety of biological samples, from cell organelles to single proteins, virtually free from any contaminations, to the focus of an X-ray laser which can be used to image them.
In a new study published in PNAS, an international research team, led from Uppsala University, discovered kin relationships among Stone Age individuals buried in megalithic tombs on Ireland and in Sweden. The kin relations can be traced for more than ten generations and suggests that megaliths were graves for kindred groups in Stone Age northwestern Europe.
The origin of giant apatite-iron oxide ores of the so-called ‘Kiruna-type’ has been the topic of a long standing debate that has lasted for over 100 years. In a new article, published in Nature Communications, a team of scientists presents new and unambiguous data in favour of a magmatic origin for these important iron ores. The study was led by researchers from Uppsala University in Sweden.

There are no signs that hybrids of dog and wolf have contributed to the Scandinavian wolf population – a matter that has been discussed, especially in Norway. These wolves appear to have originated from the Nordic region or adjacent parts of Northern Europe, new genetic research from Uppsala University shows.
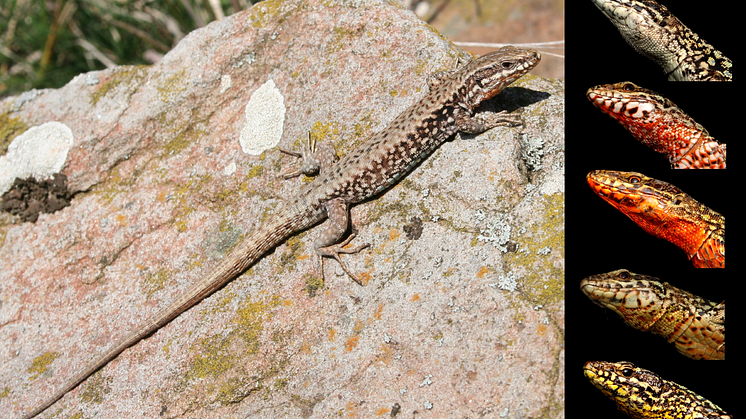
How are reptiles capable of generating such a diversity of bright colors? And how is it possible that within a single population of the same species, different individuals exhibit strikingly different coloration patterns? A team of scientists reveal two genes implicated in yellow to red pigmentation in reptiles, and demonstrate that these “pigmentation genes” also affect behaviour and other traits

A world moving from fossil fuels to renewable energy will rely more and more on energy storage and in particular on batteries. The Battery 2030+ large-scale research initiative will gather leading scientists in Europe, as well as the industry, to achieve a leap forward in battery science and technology.
Coprolites, or fossil droppings, of the dinosaur-like archosaur Smok wawelski contain lots of chewed-up bone fragments. This led researchers at Uppsala University to conclude that this top predator was exploiting bones for salt and marrow, a behavior often linked to mammals but seldom to archosaurs.

What do we need to be able to store carbon dioxide in bedrock and thereby reduce the human impact on the global climate? At the Celsius-Linnaeus lectures on 7 February, geologist Martin Blunt and microbiologist and toxicologist Linda S. Birnbaum will present research findings on some of the biggest challenges facing humanity.
Around 56 million years ago, global temperatures spiked. Researchers at Uppsala University and in the UK now show that a major explosive eruption from the Red Hills on the Isle of Skye may have been a contributing factor to the massive climate disturbance. Their findings have been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
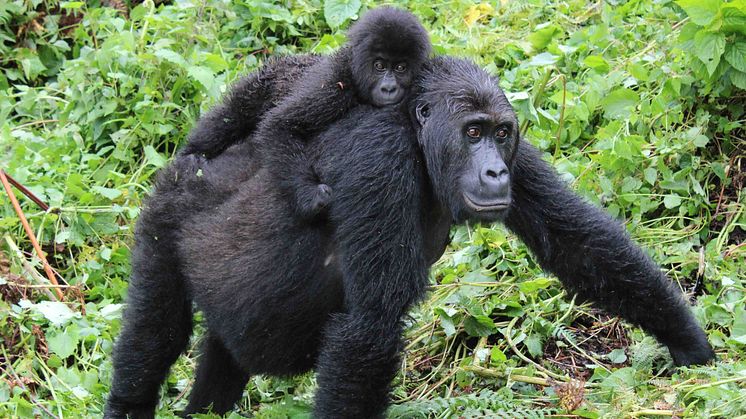
The critically endangered Grauer’s gorilla has recently lost genetic diversity and has experienced an increase in harmful mutations. These conclusions were reached by an international team of researchers who sequenced eleven genomes from eastern gorilla specimens collected up to 100 years ago, and compared these with genomes from present-day individuals. Results are published in Current Biology.

For nearly 100 years biologists have argued about how exactly natural selection can possibly work. If nature selects the individuals with the best genes then why aren’t all organisms the same? Recent findings made at Uppsala University suggest that the answer could be sex.
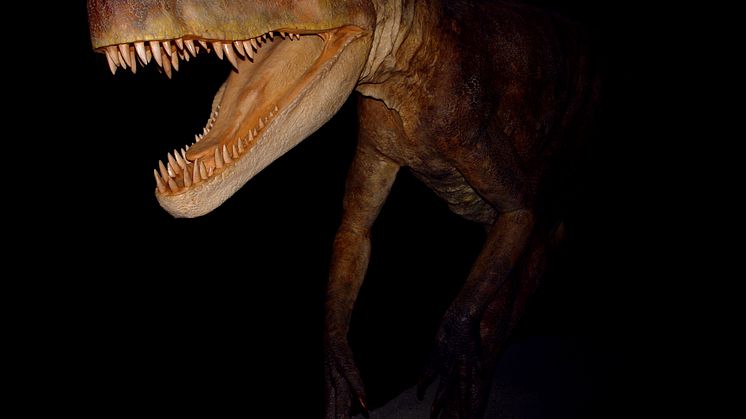
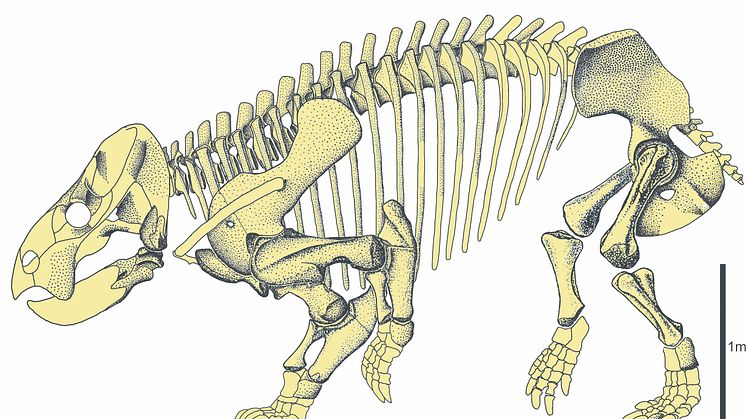
During the Triassic period mammal-like reptiles called therapsids co-existed with ancestors to dinosaurs, crocodiles, mammals, pterosaurs, turtles, frogs, and lizards. Researchers at Uppsala University in Sweden, together with colleagues in Poland, have discovered fossils from a new genus of gigantic dicynodont. The new species Lisowicia bojani is described in the journal Science.
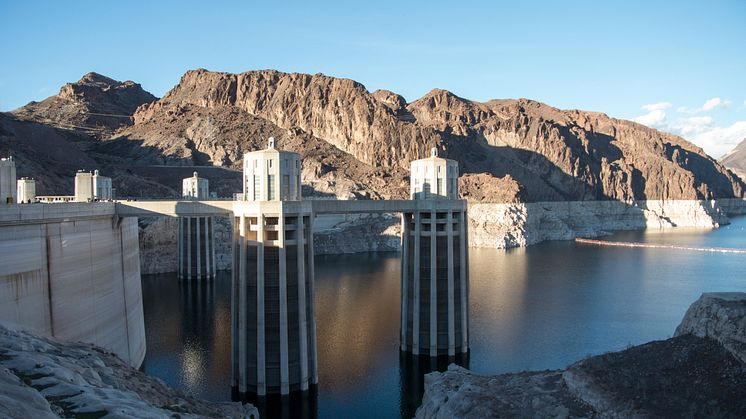
An international team of drought scientists show that while many dams and reservoirs are built, or expanded, to alleviate droughts and water shortages, they can paradoxically contribute to make them worse. The study is published in Nature Sustainability.

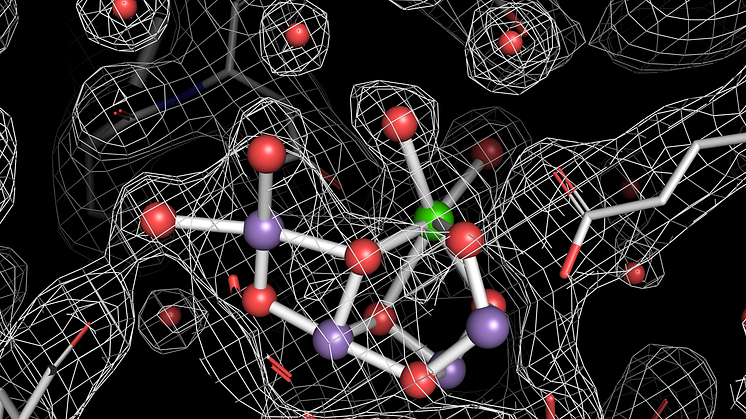
In a new article published in Nature an international research team presents high-resolution images of photosystem II, the protein complex that splits water into hydrogen ions and oxygen during photosynthesis. The images will help researchers better understand this complex mechanism, possibly opening up the door to developing cheap and efficient solar fuel devices.
Selfish genes are genes that are passed on to the next generation but confer no advantage on the individual as a whole, and may sometimes be harmful. Researchers at Uppsala University have, for the first time, sequenced (or charted) two selfish genes in the fungus Neurospora intermedia that cause fungal spores to kill their siblings.
