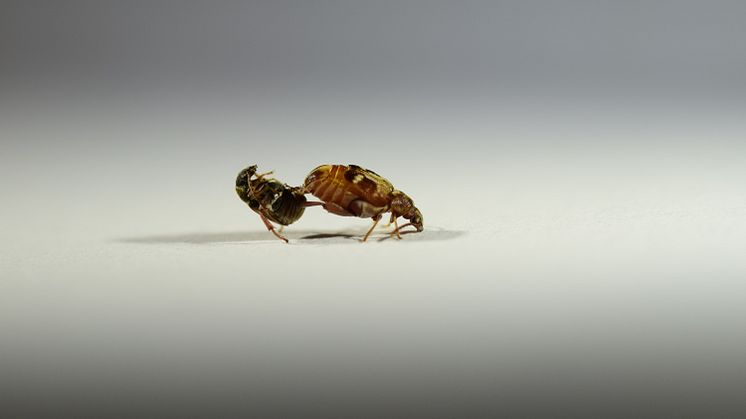
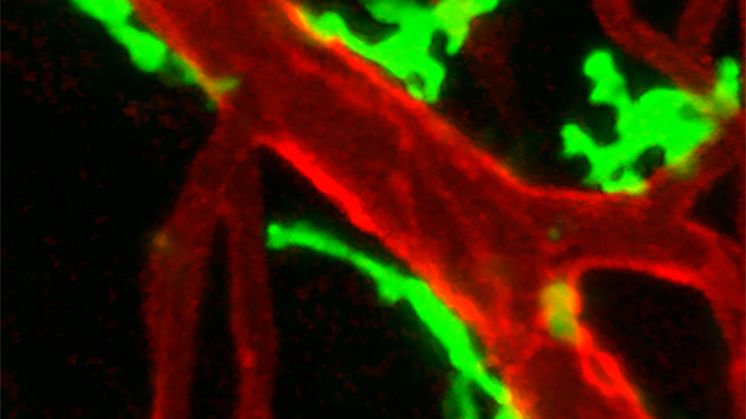
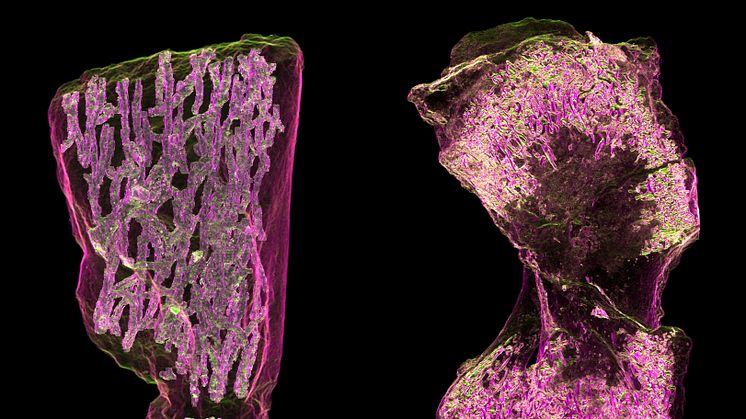
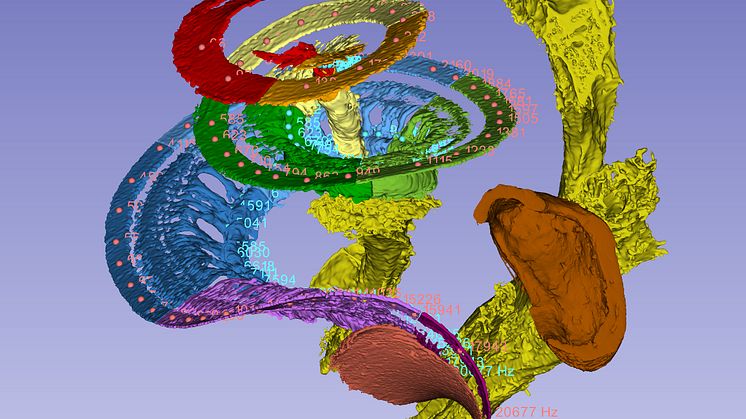
Males help keep populations genetically healthy
A few males are enough to fertilise all the females. The number of males therefore has little bearing on a population’s growth. However, they are important for purging bad mutations from the population. This is shown by a new Uppsala University study providing in-depth knowledge of the possible long-term genetic consequences of sexual selection. The results are published in Evolution Letters.