Blog post -
Radon Safety Is Rarely Expensive or Complicated
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can pose health risks if it accumulates in high concentrations indoors. However, addressing elevated radon levels is rarely expensive or complicated. With the right methods and tools, both homeowners and property managers can implement measures that are effective and affordable.
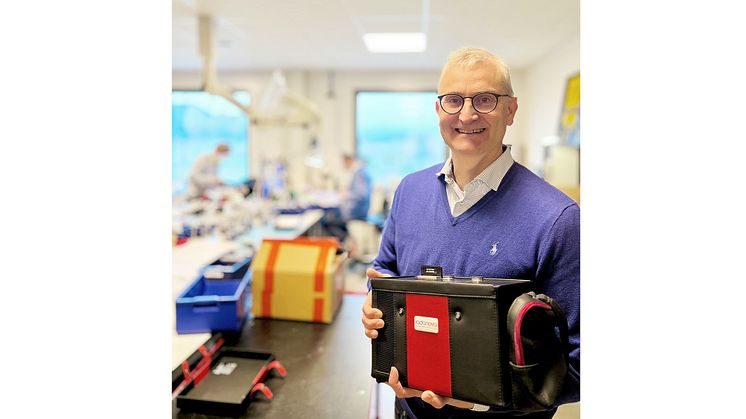
“There’s a common misconception that reducing radon levels is generally costly and time-consuming. The reality is quite different. We often see cases where elevated radon levels can be mitigated with simple measures that are economically feasible,” says Karl Nilsson, CEO of Radonova Laboratories.
Small Efforts Can Lead to Big Results
The first step to lowering radon levels in a home or building is to conduct a radon measurement. The cost of a measurement varies depending on the property, but for a single-family home, it is an easy and affordable process. If radon levels are elevated, simple measures such as improving ventilation or sealing cracks in the foundation can make a significant difference. If adjusting the ventilation isn’t enough, a radon mitigation solution will be necessary. In some countries, tax deductions or grants are available to help homeowners with radon mitigation costs.
“In many cases, it’s about minor adjustments that don’t necessarily require external expertise. The key is identifying the problem through measurement and acting accordingly,” Karl Nilsson explains.
Advanced Solutions for More Severe Issues
For properties with higher radon levels, there are more advanced but cost-effective technical solutions. Radon suction systems and radon wells are two examples of methods that can significantly reduce radon levels. A radon suction system creates negative pressure beneath the building, preventing radon from entering, while a radon well collects and vents radon before it reaches the building.
“There’s a solution for every situation. Our experience shows that costs are often lower than many expect. Of course, there are cases where more extensive measures are required, but these are relatively rare,” adds Karl Nilsson.
An Investment in Health and Property Value
Addressing elevated radon levels is not just about creating a healthy indoor environment; it’s also a long-term investment in the property’s value. Properties with documented low radon levels are often more attractive on the market. It’s important to note that the radon results documentation should come from an accredited laboratory.
Radonova, a world leader in radon measurement, has seen increased interest from property owners seeking to ensure their buildings meet guidelines. According to the World Health Organization, radon levels should not exceed 100 Bq/m³. Similar guidelines exist in most countries. Each country’s local radon authority will have information about their country-specific radon action limit.
Simple Steps Toward a Radon-Safe Environment
For those looking to reduce radon exposure and help prevent lung cancer, Radonova recommends the following steps:
- Perform a radon measurement: This is the only reliable way to identify potential issues.
- Analyze the results and locate the source of the radon leak: An accredited laboratory can help interpret the results and determine if external expertise is necessary.
- Take appropriate measures: Implement solutions yourself or with the help of experts.
Elevated radon levels don’t have to be a major concern issue. With today’s technology and methods, you can create a safe indoor environment in a simple and cost-effective way.
“Measuring and addressing radon levels when necessary has become increasingly accessible. No one today needs to live with uncertainty about radon, whether in homes or workplaces,” Karl Nilsson concludes.
It’s important to note that radon levels vary over time. To ensure safe indoor air, Radonova recommends a radon measurement every two to five years.