Blog post -
Radonloggers: SPIRIT vs ROBIN
In recent years, Radonova has developed and launched several advanced radon instruments. Among these are two radon sensors: SPIRIT and ROBIN. These instruments are quite different in terms of features and uses.
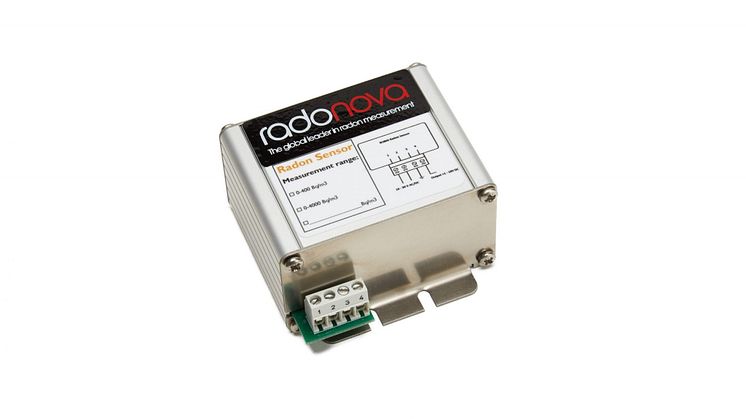
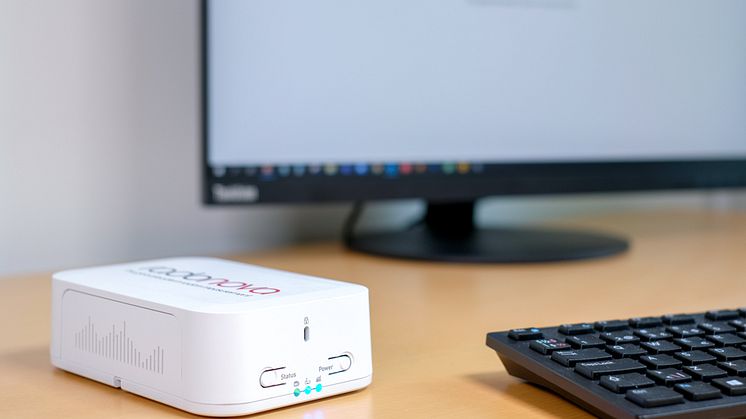
SPIRIT is a digital continuous radon monitor (CRM) for use by professionals. This highly sensitive radon sensor measures radon in real time and can be monitored remotely by customers through Radonova’s online portal. ROBIN is a radon sensor for fixed installation within homes. It is easily connected to a controller or regulator and provides an analog signal for fan control in a radon removal system.
Data transfer
One main difference between SPIRIT and ROBIN is the feature of data transfer. SPIRIT stores the data it collects in the cloud and transfers that data wirelessly. Users have access to smart analysis tools on Radonova's website portal, called “My Pages”, where the data can be downloaded to their own server through an API connection.
ROBIN is specifically developed to be built in to control systems where it measures radon and provides analog inputs to the control the system in which it is connected. It does not store data or have internet connectivity capabilities.
Measurement capabilities
In addition to radon levels, SPIRIT measures temperature, humidity and air pressure. These measurement points are then saved for two months. ROBIN, however, is an integrated sensor within the ventilation system and can provide direct control by means of cable connection.
Technology and function
Radonova radon expert Dag Sedin explains that SPIRIT is Radonova’s most advanced radon sensor with a measurement range of 1-100,000 Bq/m3. Sedin goes on to say, “The instrument stores a complete energy spectrum every 10 minutes which is analyzed on our application server immediately as the data arrives. Through the spectrometer function, the short-lived radon daughter Po-218 can be separated from the long-lived radon daughter Po-214. In this way, the response time is radically improved. Through analysis on our server, upgrades to the software can be done automatically, while it is possible to detect instrument errors through our automated troubleshooting. To monitor radon data from SPIRIT in a simple way, you can build dashboards that allow several sensors to be monitored in the same window via the computer or mobile phone browser.
ROBIN radon sensor is developed for integration into control systems. Sedin says that ROBIN “is optimal for controlling ventilation directly through an output signal of 1-10V DC which is directly proportional to the radon level in each range. It has built-in algorithms that detect non-statistically significant changes in radon data and stabilize the output signal, which makes it easier to control the ventilation system.” Dag Sedin concludes that “ROBIN is available as standard in 1-400 Bq/m3 and 1-4000 Bq/m3with the option to order customized versions with your own unique measurement range.”
ROBIN - Radoninstruments.com (EN)
SPIRIT Radonlogger - Follow-up measurement at workplaces and in homes - Radoninstruments.com (EN)