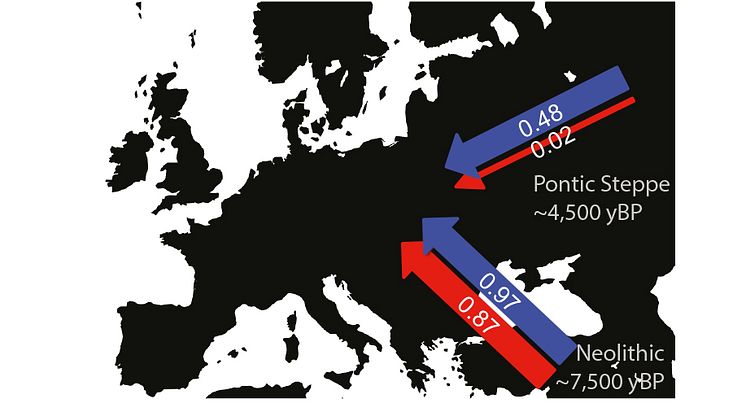
Genetic data show mainly men migrated from the Pontic steppe to Europe 5,000 years ago
A new study, looking at the sex-specifically inherited X chromosome of prehistoric human remains, shows that hardly any women took part in the extensive migration from the Pontic-Caspian Steppe approximately 5,000 years ago. The great migration that brought farming practices to Europe 4,000 years earlier, on the other hand, consisted of both women and men.