Blog post -
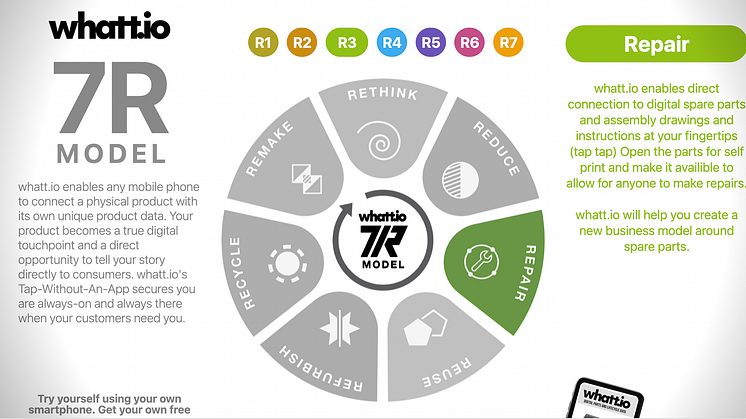
REPAIR, the revolution of digital spare parts, part 3 of the 7R model
Embracing Repair through Digital Spare Parts
In the realm of sustainable products of high quality, "repair," as an element of the circular 7R model, arguably plays the most crucial role. The recent decades have witnessed a lamentable decline in product quality, a trend detrimental to both the environment and sustainability as a whole. The essence of reducing Carbon, water, and energy footprints lies in extending a product's lifespan.
The environmental friendliness of a product is proportional to its longevity post-manufacture, potentially spanning generations. Ideally, well-designed and functional products should never turn into waste. The legendary air-cooled Porsche 911s exemplify this, their intricate hand-built structure symbolizing a generation of cars you could personally maintain, owing to their robustness and comparatively simple electronics.
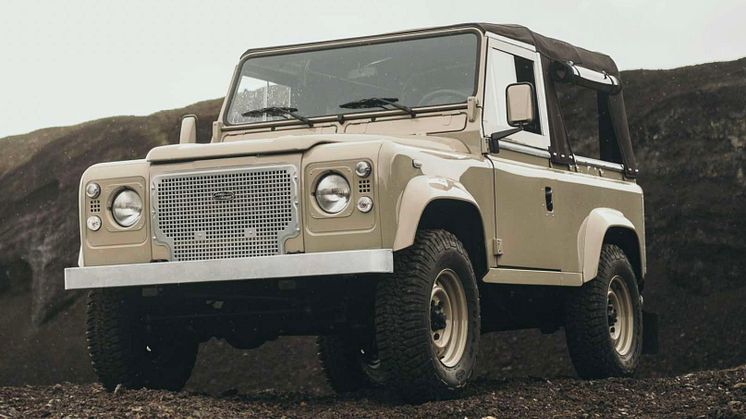
The Range Rover Defender is another model echoing this ethos, offering the owner the genuine prospect of self-maintenance.
Regrettably, these qualities are no longer the norm, transcending the automotive industry into various other sectors. Products lack repairability, not due to the difficulty in mending but because owners often lack the necessary information to undertake the repair. The inclusion of metadata, encompassing schematics, drawings, assemblies, and bills of materials, can significantly improve the repairability of products ranging from furniture to cars to dishwashers.
In many instances, manufacturers deliberately make their products difficult to repair, often neglecting to run tests and simulations that would facilitate repair, rendering the process prohibitively expensive. This leads to product waste, and consumers purchasing new items rather than repairing existing ones. However, modern 3D CAD and virtual reality tools can simulate these processes. The primary challenge lies in fostering the willingness to allow others to carry out repairs.
While manufacturers focus extensively on streamlining manufacturing processes and cutting costs, minimal efforts are invested in creating easy-to-maintain products. A truly sustainable product (or building) typically has a lifespan a hundred times longer than its production time. Thus, every opportunity to extend its life through servicing and repair benefits our planet by minimizing waste management impacts and the need for new product production.
Products should be rated based on their longevity, in addition to their energy consumption. Moreover, consumers should be informed about the actual carbon, energy, and freshwater footprints involved in producing a new product versus repairing an existing one.
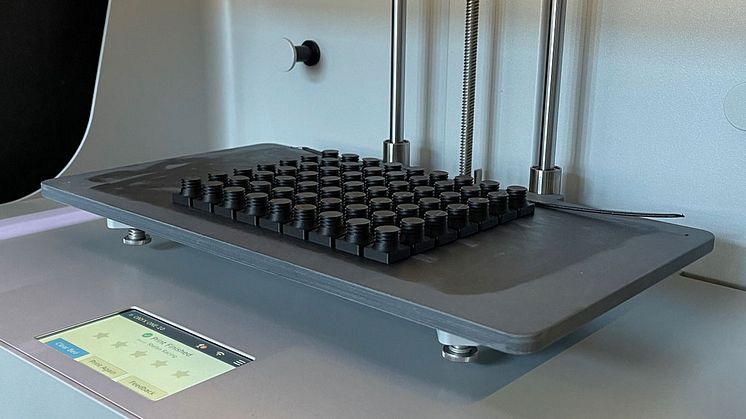
The advent of digital spare parts, particularly those locally manufactured through 3D printing or additive manufacturing, brings hope. 3D printing offers the advantage of creating what you need precisely when you need it, reducing the nonsensical mass production and storage of parts in countless locations.
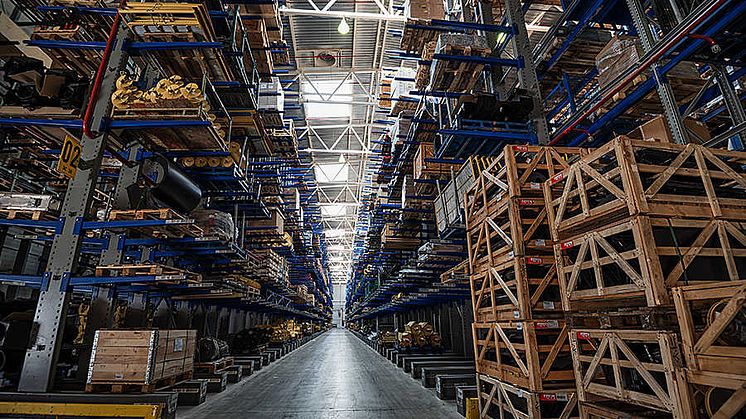
The current model of plastic parts production results in vast waste, with estimates suggesting 10% of all manufactured plastic parts — nearly 40 million tonnes out of a total of 400 million tonnes annually — never see usage and eventually contribute to waste, ending up in landfills, incineration facilities, or, in the worst-case scenario, our oceans.
A smart and efficient approach to spare parts production using additive manufacturing can alleviate this problem. However, 3D printers, the common name for additive manufacturing machines, require a digital 3D model (usually in formats like STL or 3MF) to function.
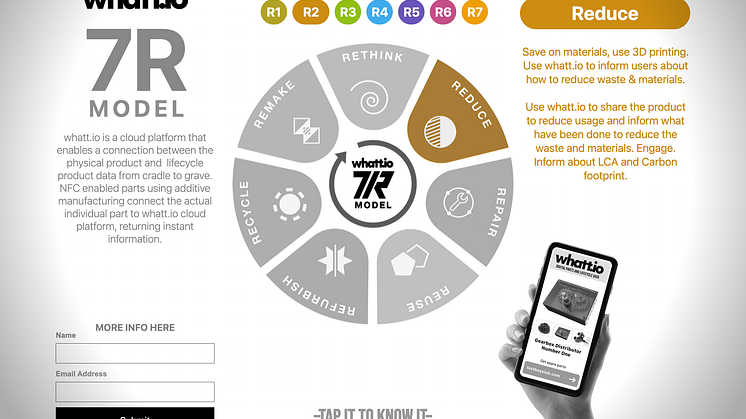
To repair a product, you need to identify the required spare parts and find them online or have them manufactured on-demand, even potentially in your garage. Platforms like whatt.io provide a solution, connecting digital parts to physical products, essentially serving as a physical metaverse. This makes obtaining the right parts as easy as tapping your mobile phone on the product and receiving a response with all relevant information.
Circular design and economy necessitate technology platforms that enable full product traceability and serve as a higher-level information platform providing end-users with valuable information when required.
When fully implemented, the digital spare parts concept can dramatically improve sustainability by extending product life cycles, reducing mass production of spare parts, and paving the way for innovative business models. whatt.io is leading the charge, connecting e-commerce platforms with spare parts and allowing the upload of 3D production models for local additive manufacturing, or even self-printing. The rise of this digital market will reward those companies bold enough to challenge the status quo, offering superior quality for less and promoting self-repair and long product lifecycles.
Just as the Metaverse and NFTs maintain digital asset ownership, allowing you to buy and sell assets, the same will apply to the 3D printing world. 3D printers operate using digital assets (the 3D production CAD model). The next evolution of these platforms will accommodate small license fees for parts production, ensuring the rightful intellectual property owner profits even from digital spare parts. This monumental shift from physical to digital spare parts eliminates the need for transportation, warehousing, and unnecessary mass production.
This transition is spurred by the positive environmental impacts and the potential for ongoing profit from parts without creating unnecessary waste.