Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
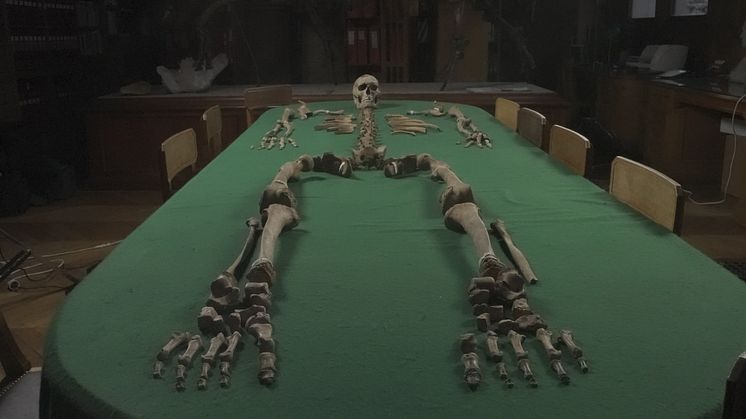
In a new study, researchers at Uppsala University have clarified family relationships in four graves from a 5,500-year-old hunter-gatherer culture at Ajvide on Gotland. DNA analyses suggest that the people were well aware of family lineages and that relationships beyond the immediate family played an important role.