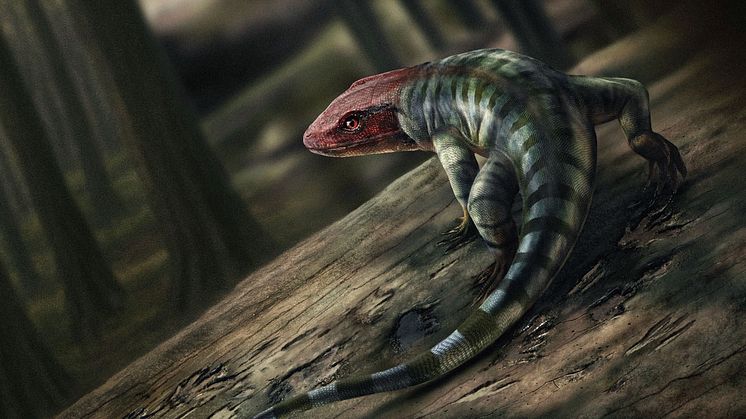
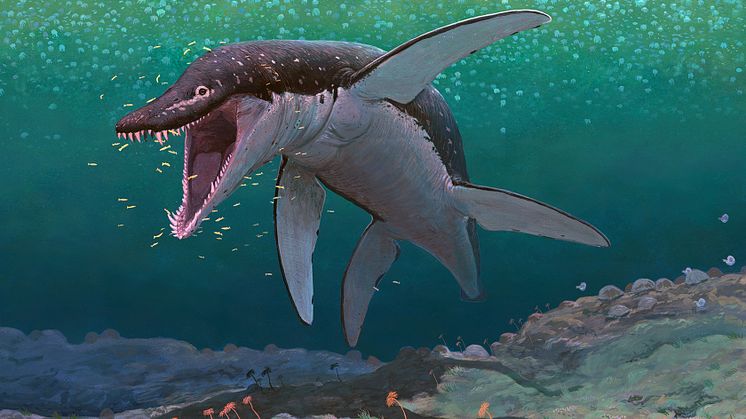
Sea reptile’s tooth shows that mosasaurs could live in freshwater
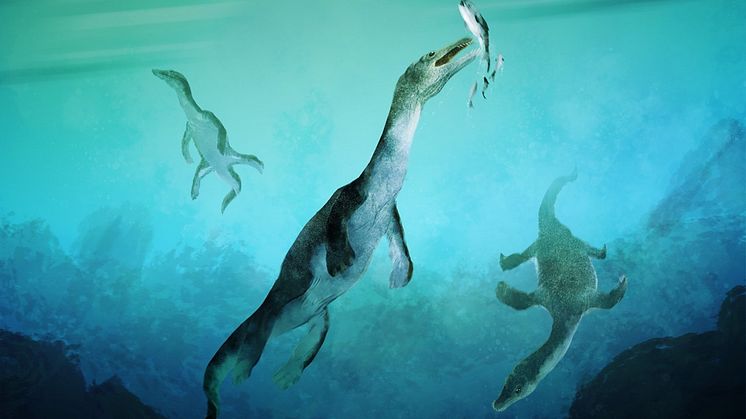
Mosasaurs, giant marine reptiles that existed more than 66 million years ago, lived not only in the sea but also in rivers. This is shown by new research based on analyses of a mosasaur tooth found in North Dakota and believed to belong to an animal that could reach a length of 11 metres.