Blog post -
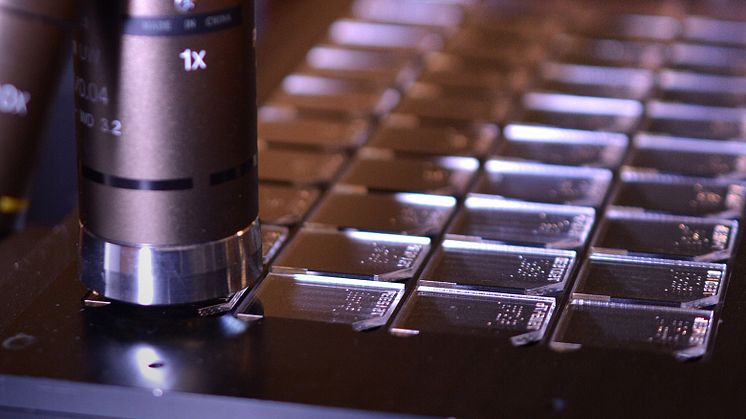
Accreditation guarantees accurate radon measurement
Accreditation guarantees the quality of a radon measurement, in part because the laboratory's measurement processes are regularly checked by independent organizations. However, most of the world's radon laboratories are not accredited, which to many might seem a little strange. Why is this? Firstly, accreditation entails a large additional cost and secondly customers do not demand it, but this is expected to change.
Why is accreditation important?
When a customer orders a radon measurement, the expectation is that the measurement is conducted professionally and accurately – a non-accredited laboratory cannot guarantee this.
– An incorrect procedure can, for example, lead to measuring too low values, although the user is actually measuring an indoor environment with high radon levels. For those who live or work in such an environment, the risk of suffering from lung cancer increases and unfortunately the individual will not be aware of this. Conversely, carrying out a measurement that incorrectly shows too high values also has undesirable consequences. This means time and money is invested to reduce radon levels even though it is not necessary, comments Karl Nilsson, CEO of Radonova Laboratories.
The conclusion is therefore obvious: always use radon measurement technology from an accredited laboratory.
What differentiates an accredited radon laboratory?
An accreditation according to the laboratory standard ISO/IEC 17025 sets a quality level for the business. This includes mandatory requirements for quality systems and competence.
Factors that differentiate Radonova from other providers:
- Our measurement processes are continuously revised by an independent government agency. They check that we meet different measurement standards and ISO/IEC 17025. In Radonova's case, it is SWEDAC, the national accreditation body for Sweden, that continuously tests that the company is competent to carry out the accredited tests.
- We are monitored for impartiality – there should be no self-interest for Radonova to provide a certain measurement result. For example, if you conduct radon consulting, it could be tempting to show too high values because it would generate more jobs. We do not do that.
- We continuously calibrate our measuring equipment and radon detectors against a known radon source, e.g. Radon chamber of the Radiation Safety Authority.
- We participate in demanding national and international comparison tests.
Note, accreditation may relate to different measurement methods. Therefore, it is important to check what types of measurements a laboratory is accredited for. Radonova is accredited for both indoor air and water measurements.
Here you will find more information about Radonova and our accredited measurement methods.
Customers can trust a measurement from Radonova
Since October 1995,Radonova has been an accredited test laboratory for radon. This means that we can guarantee high quality and accurate radon measurements. With accreditation and the market's fastest delivery and analysis times, we have become the first choice for individuals and businesses who want to carry out a correct radon measurement as efficiently as possible.