Blog post -
New Builds – the importance of measuring for radon in soil
When radon is being discussed, it frequently revolves around levels of radon in soil. This is not surprising. Radon leaking or being sucked from the ground is the cause of elevated indoor radon levels in 80 per cent of affected properties. However, it is important to note that radon content in the soil where the building is located, does not necessarily determine indoor radon levels. In most cases, the materials used to build the home, and the design of the ventilation system, influence the presence of radon in the dwelling. Builders and designers should always be mindful of radon when planning a new property.
If there are high levels of radon in the soil, a radon guard should be incorporated into the design of the home from the outset.
Radon content in different soil types
In order to manage potential radon issues in regard to new builds, you need to understand how radon is formed and where it exists. Radon is a decay product from the radioactive element Radium, which in turn is a decay product of Uranium, found naturally in soil. As radon is a gas it easily leaks from the soil into houses through tiny cracks in foundations and walls. However, concentrations vary, which affects radon levels in different types of soil. In some cases, high levels of radon naturally occur due to the precipitation of uranium and radium from groundwater.
Another important factor to consider is the shape of the mineral grains in the soil. Generally, radium-containing grains with a large exposed surface cause more radon. The surface size usually increases with a smaller grain size and with greater cracking in the grains. In addition, radon content in soil is affected by how it spreads from the ground to the atmosphere, which is controlled by the soil's porosity, water content and winds. Therefore, radon levels are often weather dependent.
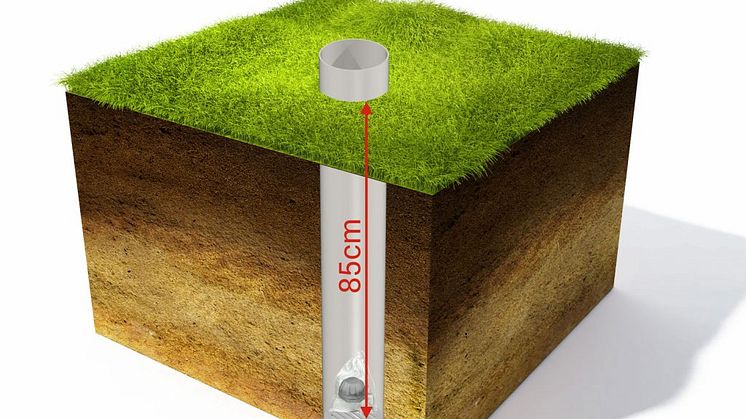
The only way to fully understand how much radon is in the soil is to measure. In order to minimize the impact of variable weather conditions, the measurement should be done at a depth of 0,8 – 1 meter. Two measurement methods are used to do this - digital and passive.
In the long term, it is more cost effective and efficient to have an accurate measurement from the start, especially in relation to new builds. Therefore, in terms of radon, make sure it is a consideration at an early stage. It pays off.
For more information about radon and radon measurement please visit www.radonovalaboratories.com