Blog post -
What are acceptable levels of radon gas exposure?
The effects of radon gas exposure on our health are well documented and have been proven to be life threatening. In fact, Radon gas exposure is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. Therefore, long-term exposure to the gas increases the probability of developing lung cancer.
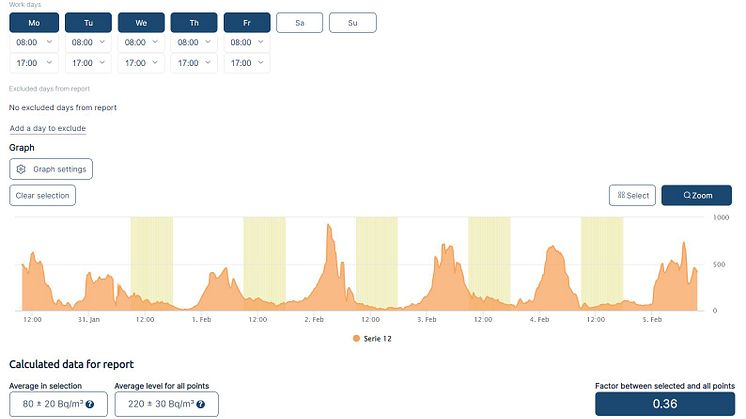
Any exposure to radon gas provides a risk, even is that exposure is reasonably low. The key message is that we must measure radon levels in our homes and workplaces and keep them as low as possible.
However, there are national and international legislations which have been set up which outline acceptable levels of radon gas exposure. These levels can be reference levels or action levels, and they differ from country to country.
One of the first legislationswas the European Union’s EURATOM Directive 59/2013 “Basic Safety Standards”. The document’s intention is to protect EU citizens from the dangers arising from ionizing radiations and radon exposure was part of that Directive. The reference level is 300 Bq m-3 in terms of annual radon activity concentration.
EU members states are advised to implement the reference level into their national legislations. Most of the countries have adopted 300 Bq m-3, however some have decided on a lower value of 200 or 100 Bq m-3.
In addition to that, the EURATOM BSS Directive established a limit in terms of radon dose exposure. The number is six mSv per year. If the dose is above that limit, it should be treated as a planned exposure situation.
In the US, the action level is four pCi l-1 or 148 Bq m-3, but it is not mandatory at a federal level. Nevertheless, most states have included this value in state legislation.
Finally, WHO and IAEA also have levels for radon exposures. WHO considers that radon exposures should not be above 100 Bq m-3. IAEA has in its document, IAEA Basic Safety Standards, 300 and 1000 Bq m-3. The differential depends on the exposure type: occupational or residential.
To conclude, it is essential to be aware of the level that applies to where you live or work. Bear in mind that the ultimate objective is to keep radon levels as low as possible. Remember the effects of radon exposure are long-term. Therefore, it is necessary to periodically verify radon levels at home or work.
Contact us here if you require further information.