Blog post -
Should I be worried about temporarily high radon levels?
Radon levels in a house can vary considerably over 24 hours, and will be different depending on the day you take the measurement. However, if you consider the possibility of being exposed to elevated radon levels over a 10 to 20 year period, then the risk of developing lung cancer increases. Therefore, don’t worry about temporarily elevated radon levels just being above the limit value of 200 Bq/m³. Instead, it is the long-term average that matters.
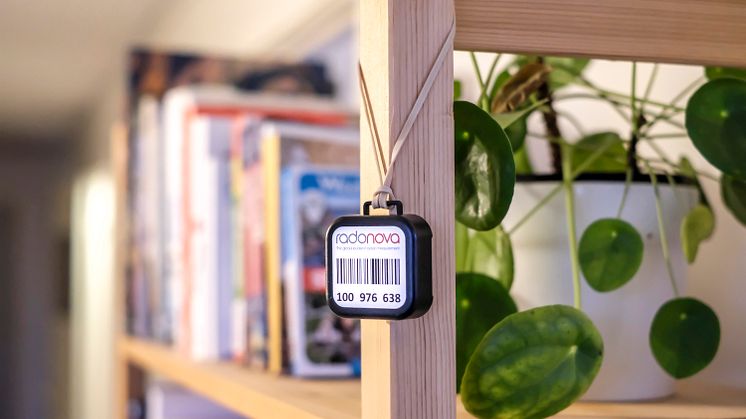
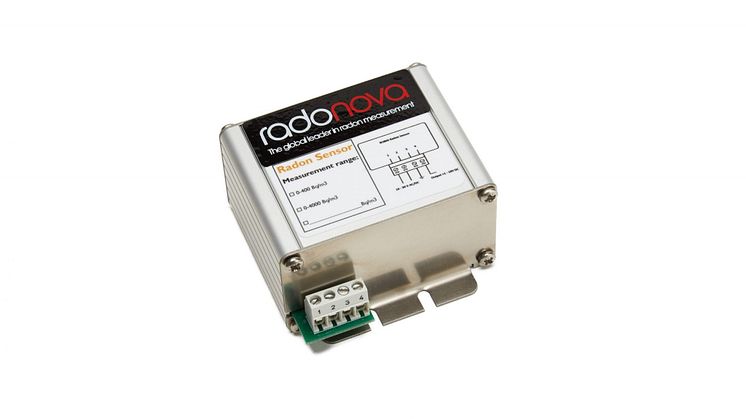
If a measured annual average value is above the limit value, it is important to implement radon-reducing procedures. An annual average value is obtained by measuring radon levels via an accredited laboratory over a long-term period. If you measure for radon with a digital radon instrument over one or two days you will not get an accurate result. However, this type of instrument can be used to analyse if radon reducing measures are working.
Why do radon content levels vary during a day?
The fact that radon levels change during a day can be down to several factors. Here are some reasons:
How we live - air remains dormant when no one is at home, or when homeowners are sleeping at night – which can lead to elevated radon levels. This is in contrast to when you move around the house, creating more circulation which renews the air.
Ventilation - just as humans affect the properties of air, so does ventilation. It may not be so important in a house, but in a workplace with time-controlled ventilation, it can have a massive impact.
Weather - changing temperatures and wind can affect the pressure difference between indoor air and ground air. This is important because radon traditionally leaks into the house from ground air. If temperature differences and wind cause negative pressure in the house, indoor radon levels are likely to increase.
Property location – elevated properties may be susceptible to greater variations in radon levels during the winter. This is due to thermal rising in the ground.
Naturally, there can be other reasons which influence radon content in houses, for example if you have doors open to the basement, or use a cooker hood or fireplace.